Figure 6.
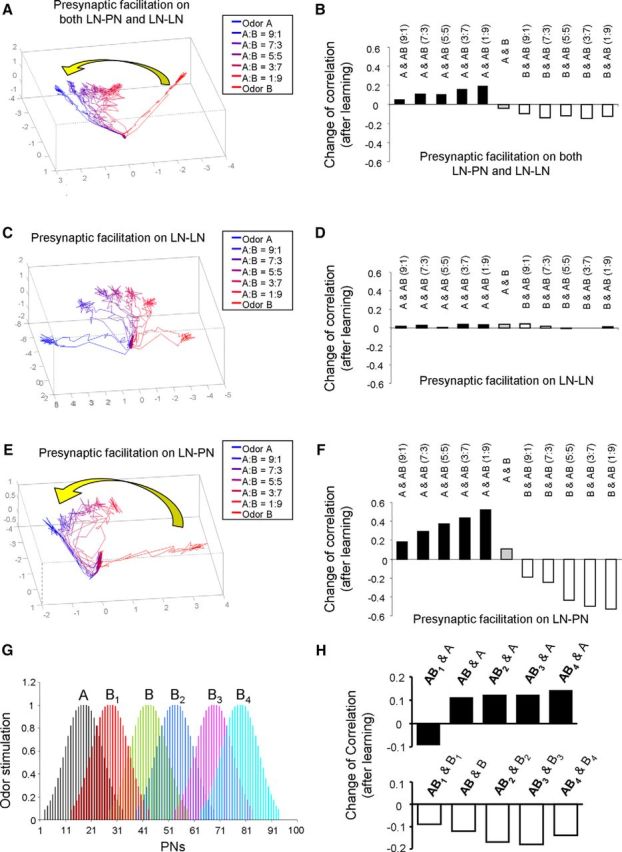
Changes of odor responses in AL after learning based on presynaptic facilitation. A, After learning of odor A manipulated by presynaptic facilitation in both LN-PN and LN-LN synapses, the dynamic trajectories of odor responses based on activities across all PNs are presented in 3D PCA space. The trajectories of mixtures were found to shift closer to the trajectory of learned odor, odor A. B, Corresponding to A, the change of correlation coefficient derived before and after olfactory learning was also calculated. It was found that, after learning of odor A, the correlation coefficient between odor A and mixture odors increased. On the other hand, the correlation coefficient between odor B and mixture odors reduced. C, In the second setting, the presynaptic facilitation mechanism was installed in LN-LN synapses only. In PCA space, the trajectories of mixture odors stay at the middle between the trajectories of odor A and odor B after learning without obvious shift toward either pure odor component. D, Corresponding to C, the change of correlation coefficient between odor responses was quite small after learning. E, In the third setting, the presynaptic facilitation mechanism was installed in LN-PN synapses only. The trajectories of mixture odors in PCA space were found to move toward the learned odor, odor A. F, Corresponding to E, the correlation coefficients between odor A and mixture odors were increased significantly after learning. On the other hand, the correlation coefficients between odor B and mixture odors were decreased. G, The spatial patterns of alterative odor B (including B1, B2, B3, and B4) were plotted. These alternative odors were also used to test the impact of presynaptic facilitation on olfactory responses. H, Following G, the degree of similarity between pure odor and mixture odor (5:5) responses was evaluated by correlation coefficients across PNs. Top, The correlation between mixture odors and odor A increased after learning of odor A, except one of the mixture odors, AB1. Bottom, The correlations between all mixture odors and odor B reduced after learning of odor A.
