Figure 1.
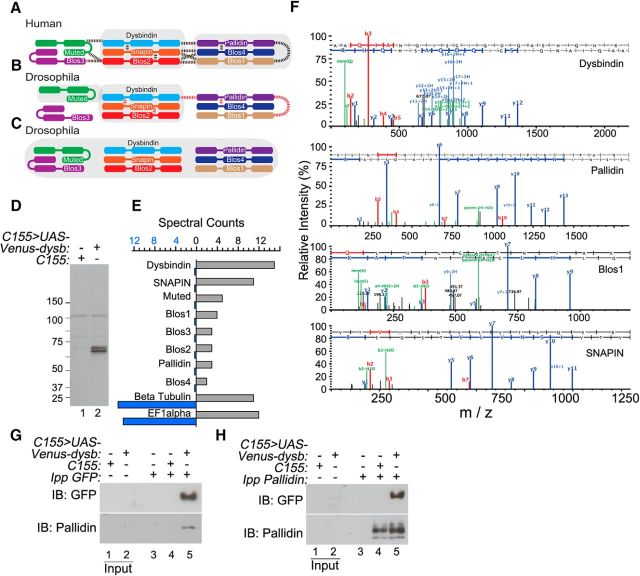
BLOC-1 assembles into an octameric complex in Drosophila neurons. Previously identified mammalian (A) and Drosophila (B) BLOC-1 subunit interactions. Dotted lines represent interactions identified by yeast two-hybrid (dotted lines), while shaded regions depict complex or subcomplex formation based on immunoprecipitation or cosedimentation studies. Identification of Drosophila BLOC-1 subunits immunoprecipitating Venus-Dysbindin is consistent with octameric mammalian BLOC-1 architecture (C). Immunoblot with GFP antibodies confirms expression of the Venus-Dysbindin transgene from fly head lysates in animals expressing the transgene (lane 2) but not control animals (lane 1; D). Lysates as shown in D were immunoprecipitated using GFP antibodies. Spectral counts of all eight BLOC-1 subunit orthologs were selectively enriched following immunoprecipitation with GFP antibodies from animals expressing the Venus-Dysbindin transgene (E, gray bars) compared with controls (E, blue bars). Proteins nonspecifically bound to the GFP beads such as β-tubulin and elongation factor 1α (EF1α) were represented with similar spectral counts in both samples (E). MS/MS peptide sequencing of select immunoprecipitated Drosophila BLOC-1 subunit orthologs (F). Specific detection of BLOC-1 ortholog Pallidin by immunoblot in Venus-Dysbindin-expressing fly head lysates immunoprecipitated with GFP antibodies (G, lane 5). Pallidin antibodies precipitate Venus-Dysbindin from Venus-Dysbindin-expressing fly head lysates detected with GFP antibodies (H, lane 5).