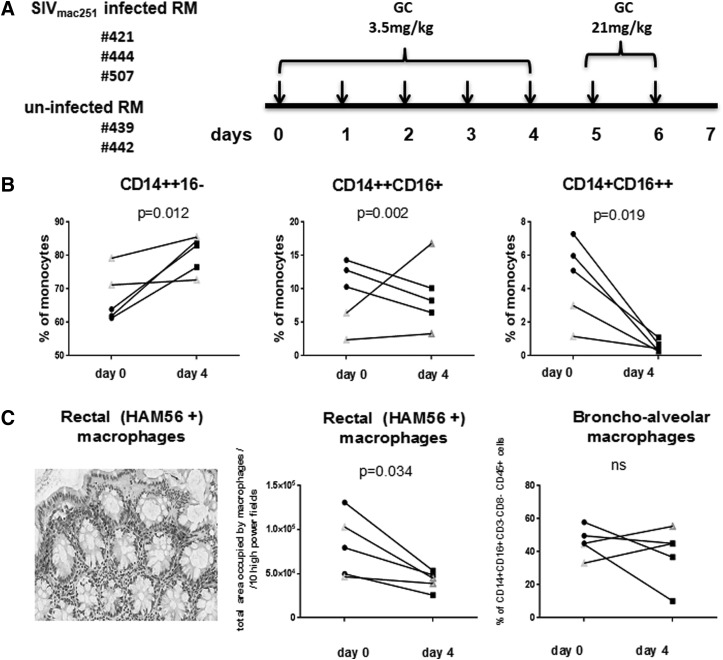
FIG. 3.
In vivo treatment of macaques with a high dose of GC. Schematic representation of the first study. (A) Three SIVmac251-infected RM and two uninfected RMs were treated for 4 days with 3.5 mg/kg GC and the remaining 2 days with 21 mg/kg GC. After 7 days, animals were sacrificed. Frequencies of CD14++CD16−, CD14++CD16+, or/and CD14+CD16++ monocytes before and after 4 days of GC (B) treatment. Filled symbols represent SIV-infected macaques. Open symbols represent uninfected macaques. The p-values were calculated for SIVmac251-infected animals (n=3). Detection of rectal macrophage by staining with HAM56 antibody (left panel) (C). Analysis of total area occupied by HAM56-positive rectal macrophage per 10 high-power fields before and after GC treatment (middle panel) (C). Frequencies of CD14+CD16+CD3−CD8−CD45+ bronchoalveolar macrophage before and after GC treatment (right panel). (C) Filled symbols represent SIVmac251-infected macaques; open symbols represent uninfected macaques. The paired t-test was used in the statistical analysis.