Figure 9. HIP/RPL29 binding involves multiple structural features of HS.
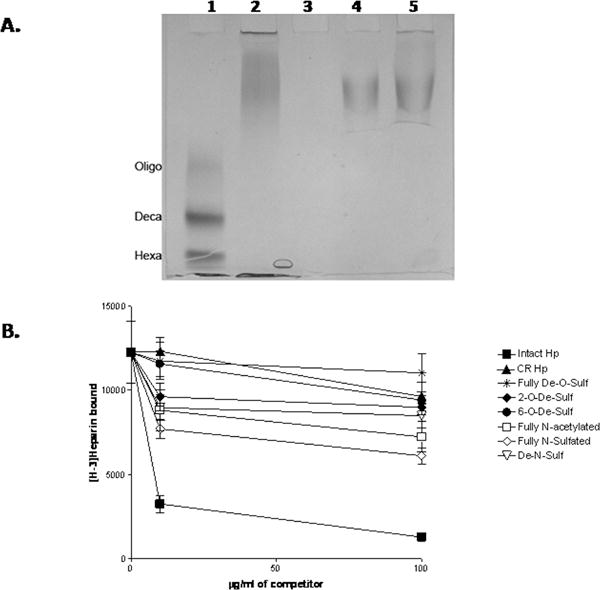
Panel A: HS heparitinase protection assays and gel electrophoresis were performed as described in Materials and Methods. Lane 1 shows the migration position of HS MW standards including an HS oligosaccharide mixture (Oligo) with a median MW of 4.2 KDa, an HS decasaccharide (Deca) and an HS hexasaccharide (Hexa). Lane 2 is HS incubated with buffer only. Lane 3 shows the products obtained after HS digestion with heparitinases. Lanes 4 and 5 are the products obtained after heparitinases digestion in the presence of 5 μg/ml and 40 μg/ml HIP/RPL29, respectively. Note that the products are essentially the same size as the undigested HS. Panel B: [3H]-Heparin was bound to HIP/RPL29 in a solid phase binding assay in the presence of the indicated concentrations of heparin derivatives and bound [3H]-heparin measured as described in Materials and Methods. The graph points each indicate the average +/− SD of duplicate determinations in each case. Symbols: ▼, fully D-O-sulfated; ▲, carboxyl reduced; ●, 6-0-de-sulfated; ◆, 2-0-desulfated; ▽, De-N-sulfated; □, fully N-acetylated, △, fully N-sulfated; ■, intact.
