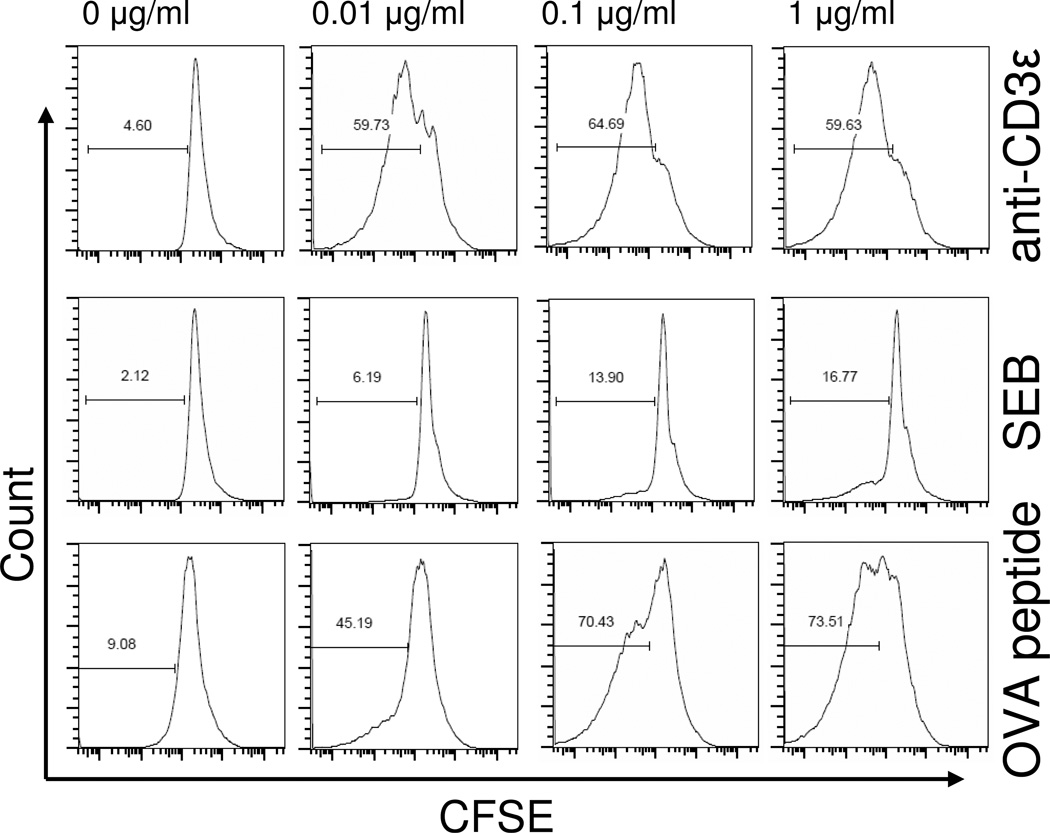
Figure 4. CD4+ T cell proliferation following stimulation with anti-CD3ε mAb, SEB, or OVA-peptide.
To confirm the biological activity of stimuli used in this study, we tested the ability of anti-CD3ε mAb, SEB, or OVA323–339 peptide to induce CD4+ T cell proliferation. Proliferation was assessed by measuring the dilution of fluorescence intensity in CFSE-stained cells using flow cytometry. Representative histograms show the percentage of proliferated, FACS-gated CD4+ T cells following 72 hours of stimulation of splenocytes prepared from WT or OT-II transgenic mice. Stimulation with anti-CD3ε mAb or OVA-peptide caused a marked concentration-dependent proliferation of CD4+ T cells (rows 1 and 3), while stimulation with SEB induced only 17% (row 2) at the highest concentration tested (1 µg/ml). Plots are representative of spleen cells prepared from 3 individual mice per group.