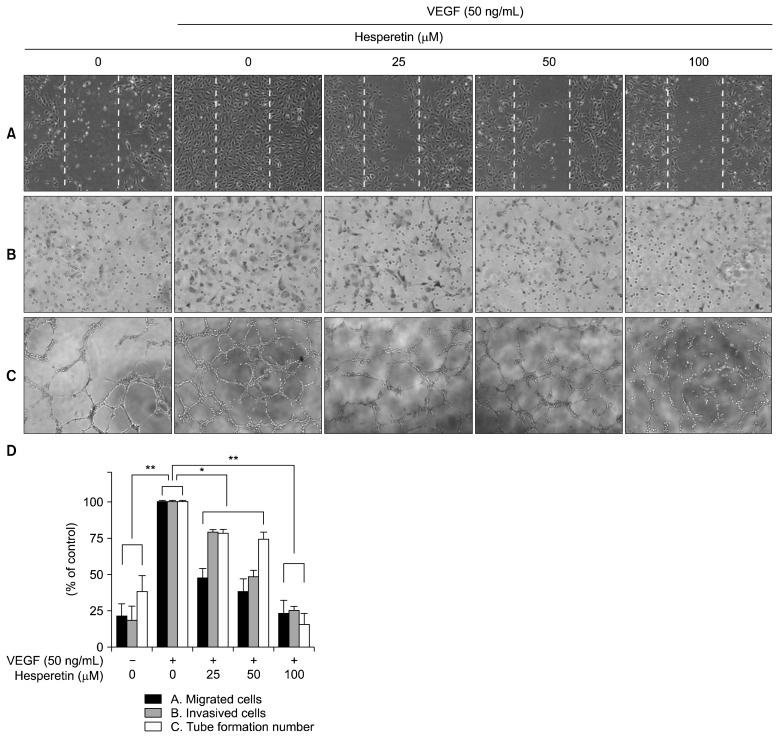
Fig. 4.
The effects of hesperetin on the migration and capillary structure formation of VEGF-induced HUVECs. (A) Hesperetin inhibited HUVECs migration. Cells were grown to confluency in six-well plates, wounded, and treated with the indicated concentrations of hesperetin and VEGF (50 ng/mL). (B) Hesperetin inhibited endothelial cell migration using Transwell migration assay. HUVECs treated with several doses of hesperetin were seeded in the upper chamber, and the bottom chamber was filled with EBM medium containing VEGF (50 ng/mL). The cells with an irregular shape in the images are cells that migrated into the lower chamber. (C) Hesperetin inhibited the tube formation of VEGF-induced HUVECs. Cells were placed in 96-well plates coated with Matrigel. After 4~8 h in the absence and presence of hesperetin, the tubular structures were photographed. The migrated cells were quantified by manual counting. (D) Calculation of cell number for migrated, invasive, and tube formations in VEGF-induced HUVECs depend on hesperetin treatment. The results are reported as the mean±SD. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 versus VEGF-stimulated cells.