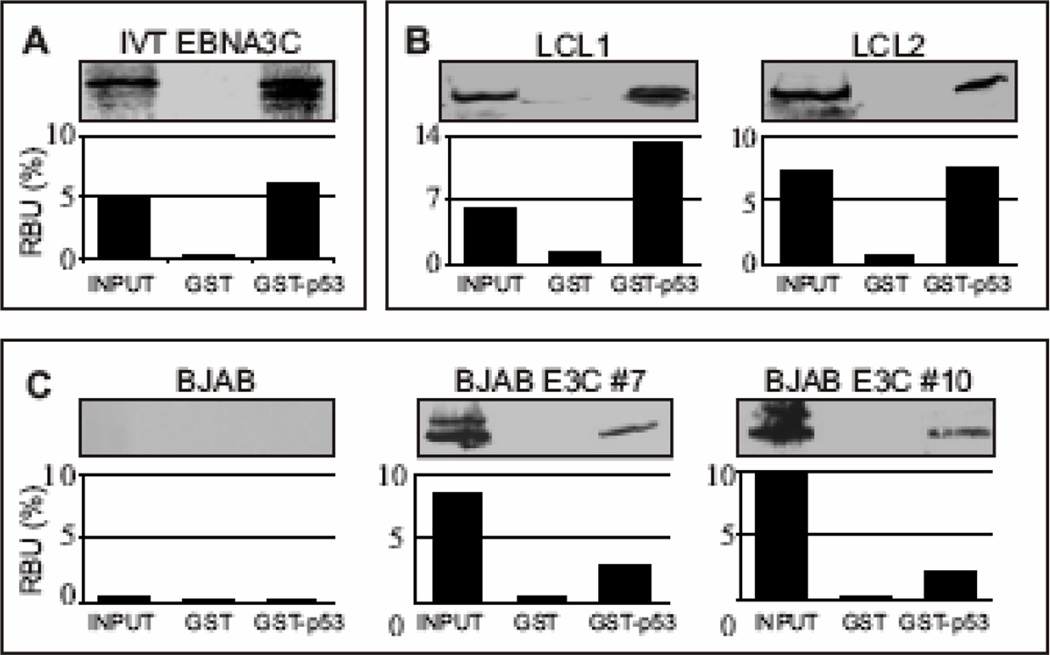
Figure 1.
EBNA3C forms a stable complex with p53 in vitro. (A) GST-p53 fusion protein was expressed in E. coli and purified with glutathione Sepharose beads. Full-length EBNA3C was labeled with 35S methionine by in vitro translation and incubated with either GST control or GST-p53 beads normalized by Coomassie staining. 5% of in vitro translation (IVT) input was used for comparison. Precipitated proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE, and bands were visualized with a phosphorimager screen. Relative Density was quantified using Storm 850 imaging system. (B–C) Either GST control or GST-p53 beads were incubated with lysates prepared from either 50 million B) lymphoblastoid cell lines (LCL1 and LCL2) or C) BJAB cells and BJAB cells stably expressing EBNA3C (two clones – BJAB EBNA3C#7 and BJAB EBNA3C#10). Approximately 5% of the lysed cells were saved as input and precipitated protein complexes were resolved by 7% SDS-PAGE. EBNA3C was detected by western blot with the specific monoclonal antibody (A10) followed by an infrared tagged secondary antibody and scanned using Odyssey imager. All panels are representative gels from similar repeat experiments.