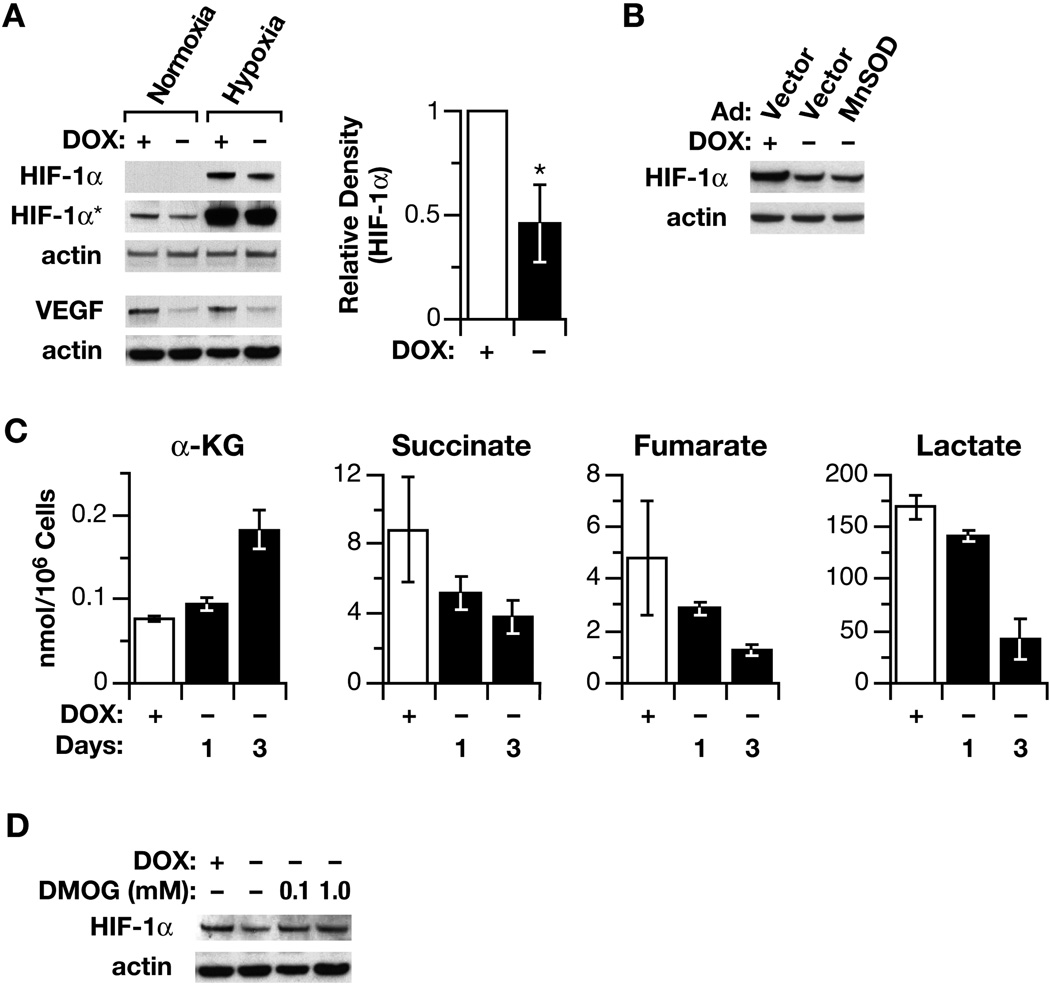
Fig. 5.
The affect of POX on HIF signaling and TCA cycle intermediates. (A). The inhibition of HIF-1α and its downstream gene VEGF was demonstrated by Western blots in both normoxic and hypoxic conditions (1 % of O2). The relative average densitometric data of four Western blots to HIF-1α in normoxic condition were also shown (B). To determine the effect of ROS/superoxide on HIF signaling, MnSOD was introduced by an adenovirus vector, which did not reverse the POX effect on the expression of HIF-1α. (C). DLD-POX cells were plated with doxycycline. After 18 h, fresh medium with or without doxycycline was substituted for the plating medium. Levels of α-KG were determined by high-pressure liquid chromatography. Levels of succinate, fumerate, and lactate were determined by GC/MS. Data are expressed as nmol/106 cells and represent the mean ± SD of at least 3 determinations. (D) The effect of DMOG on HIF-1α levels was demonstrated by Western blots. The asterisks indicated statistically significant difference (**p < 0.01. HIF-1α* indicated longer exposure).