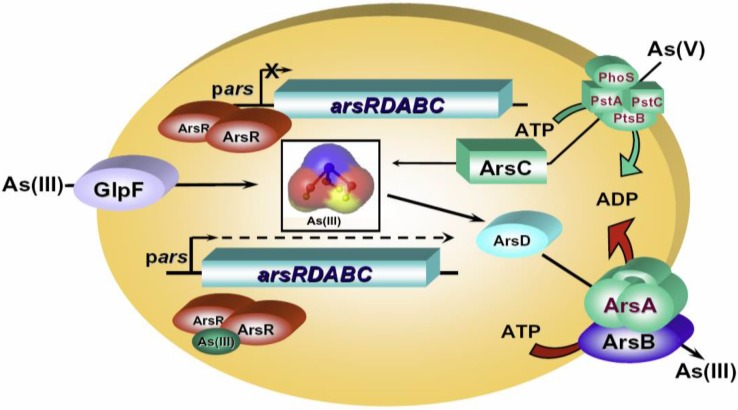
Figure 1.
The ars operon of E. coli plasmid R773. Arsenic enters cells as either As(III) or As(V). As(III) is taken up by the aquaglyceroporin, GlpF, and As(V) is taken up by pst and pho phosphate permeases. The R773 ars operon has five genes, arsRDABC. ArsR is an As(III)-responsive transcriptional repressor that binds to the ars operator/promoter to prevent transcription in the absence of As(III). In its presence, ArsR binds As(III) and dissociates from the ars DNA, allowing the expression of the ars genes. ArsD is an As(III) chaperone that delivers it to the ArsA ATPase, the catalytic subunit of the ArsAB efflux pump. ArsC is a reductase that transforms As(V) to As(III).