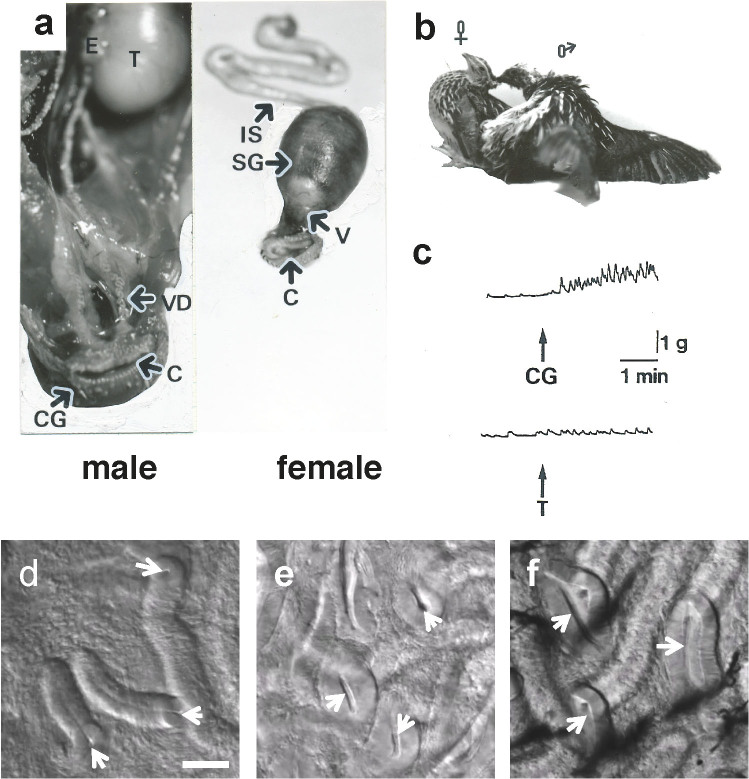
Figure 1. The reproductive system in the male and female Japanese quail.
(a), Male, T. testis; E. epididymis; VD. vas deferens; C. cloaca; CG. cloacal gland. Female, IS. isthmus; SG. shell gland; V. vagina; C. cloaca. (b), The copulatory behavior of Japanese quail showing the cloacal contact movement. (c), Bioactivity of the crude extract derived from the cloacal gland (CG) or testis (T) on spontaneous contractions of the isolated female vagina (V). The upward arrow indicates application of the extract to the tissue. (d–f), Microscopic observation of the entrance of sperm storage tubules (SST). Mature females were intra-vaginally injected with (d), 30 μl phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), (e), cloacal gland secretion (CGS) or (f), 2 × 10−9 M prostaglandin F2α (PGF2α). After 10 min injection, the mucosa of utero-vaginal junction was isolated and observed under light microscope. Arrows indicate the entrance of SST. Bar = 50 μm.