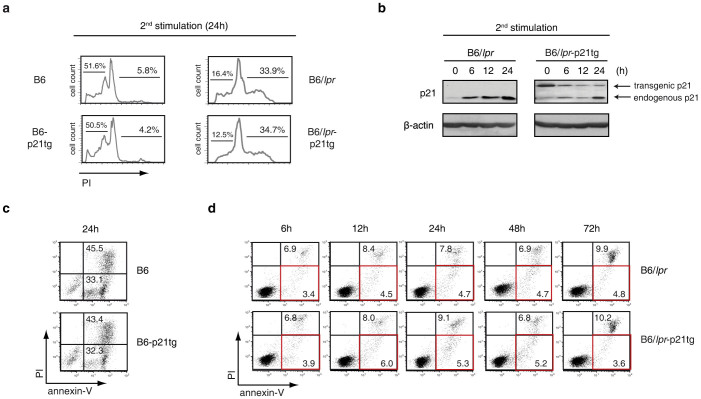
Figure 5. Apoptosis defect in B6/lpr T cells is unaffected by p21 overexpression.
(a) Purified CD4+ T cells from B6, B6-p21tg, B6/lpr and B6/lpr-p21tg mouse spleens were ConA-stimulated and -restimulated after the IL-2 expansion phase. Cell cycle analysis at 24 h after restimulation showed similar levels of cell death (presence of an apoptotic hypodiploid peak in cell cycle profiles) in B6 and B6-p21tg T cells. Lack of the apoptotic peak was similar for B6/lpr and B6/lpr-p21tg T cells. Representative histograms are from three independent experiments. (b) Western blot analysis showing endogenous and transgenic p21 protein levels at the end of the IL-2 expansion period (0 h) and at several points after ConA restimulation of B6/lpr and B6/lpr-p21tg T cells. β-actin was used as a loading control. The samples were derived from the same experiment and the two gels were run and processed simultaneously under the same experimental conditions. (c) Annexin-V/propidium iodide (PI) double staining at 24 h after ConA restimulation showed similar levels of apoptotic (annexin-V+/PI−) and post-apoptotic (annexin-V+/PI+) B6 and B6/lpr-p21tg T cells. (d) Similar cell death defects in B6/lpr and B6/lpr-p21tg T cells at various times after ConA restimulation, as shown by percentages of apoptotic and post-apoptotic events. Apoptotic T cells are shown in red squares. (c, d) Data are representative of two independent experiments.