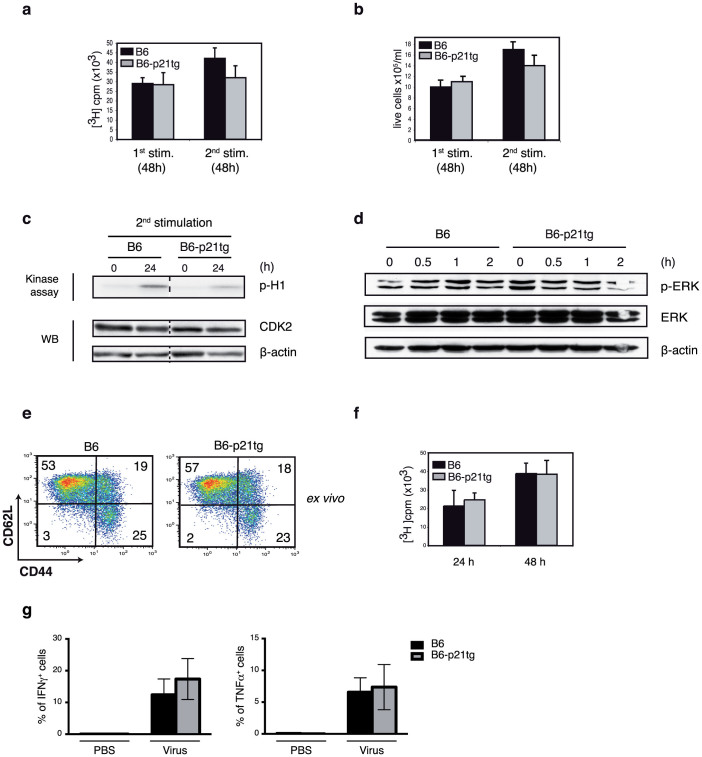
Figure 7. p21 overexpression does not affect B6 T cell proliferation or activation.
CD4+ T cells from B6 and B6-p21tg mouse spleens were ConA-stimulated or -restimulated (in the presence of zVAD) after an IL-2 expansion phase. (a) Proliferation was measured by [3H]thymidine uptake at 48 h after first or second ConA challenge. Values show mean ± SD (n = 4 T cell preparations from distinct mice). (b) Generation of newly divided B6 and B6-p21tg T cells was similar after primary and secondary stimulation, as determined by trypan blue exclusion. Values show mean ± SD (n = 3 T cell preparations from distinct mice). (c) CDK2 activity after ConA restimulation. Assay products were resolved in SDS-PAGE, and phosphorylated histone (H1) was detected by autoradiography. Extracts were analyzed by Western blot for CDK2 as loading control. Dotted line represents cropping of single gels. Full-length gels are presented in Supplementary Figure 6. (d) ERK phosphorylation and transgenic p21 protein levels in B6 and B6-p21tg T cells at various times post-restimulation. β-actin was used as a loading control. (e) Lymph nodes from OVA-immunized and –boosted B6 and B6-p21tg mice were analyzed to quantify memory CD4+ T cells. (f) Purified CD4+ splenocytes were from OVA-immunized and -boosted B6 and B6-p21tg mice were cultured with OVA and irradiated splenocytes, and showed similar [3H]thymidine uptake at 24 and 48 h postactivation. Data are representative from two experiments (n = 4 mice each). (g) Splenocytes from vaccinia-injected B6 and B6-p21tg mice were cultured with vaccinia peptide after double in vivo immunization, and showed similar specific CD8 T-cell immune responses, as detected by the proportions of IFN-γ- and TNF-α-producing cells. The non-specific responses obtained in the absence of vaccinia peptide were substracted. Data show mean ± SD (n = 5 mice).