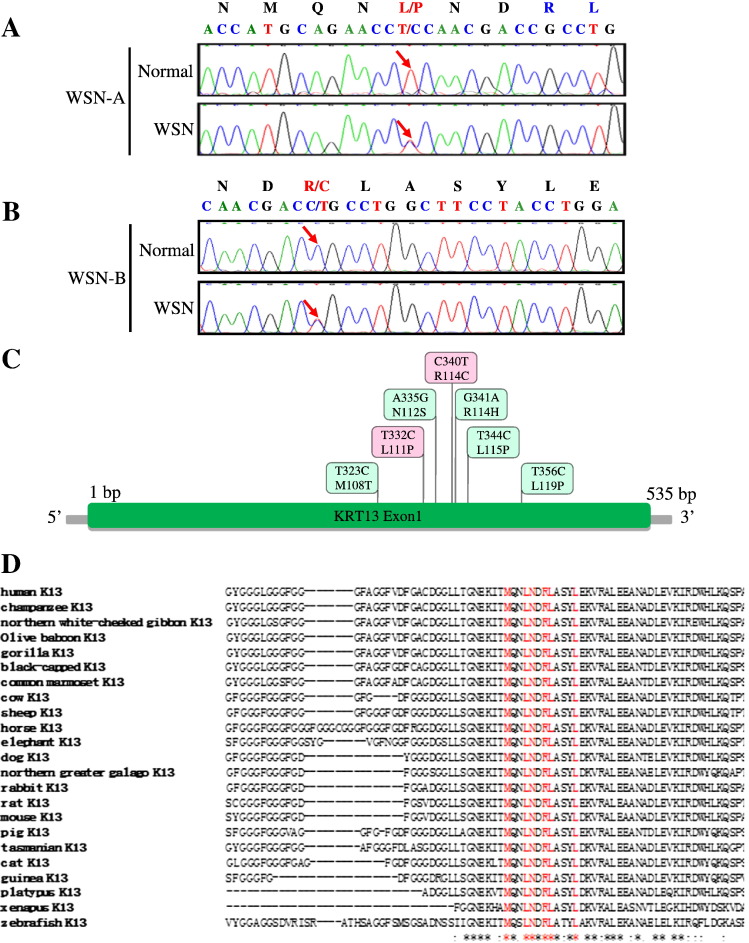
Fig. 2.
Two KRT13 mutations in two Chinese families with WSN.
(A) Partial DNA sequences of exon 1A of the KRT13 gene from the WSN-A family. The arrow indicates the position of the mutation 332T>C, the mutation predicts the amino acid change L111P in the KRT13 polypeptide from the WSN patient. (B) Partial DNA sequences of exon 1A of the KRT13 gene from the WSN-B family. The arrow indicates the position of the mutation 340C>T. The mutation predicts the amino acid change R114C in the KRT13 polypeptide. (C) The exon 1A of the KRT13 gene and the reported mutations being discovered till now. (D) A portion of the amino acid sequence of KRT13 is shown from 23 diverse species. Alignments of amino acid sequences for human, chimpanzee, northern white-cheeked gibbon, olive baboon, gorilla, black-capped chickadee, common marmoset, cow, sheep, horse, elephant, dog, northern greater galago, rabbit, rat, mouse, pig, Tasmanian devil, cat, guinea pig, platypus, xenopus and zebrafish KRT13 proteins. Red means published associated mutations in KRT13 gene; “*” means that the residues or nucleotides in that column are identical in all sequences in the alignment; “:” means that conserved substitutions have been observed; “.” means that semi-conserved substitutions are observed.