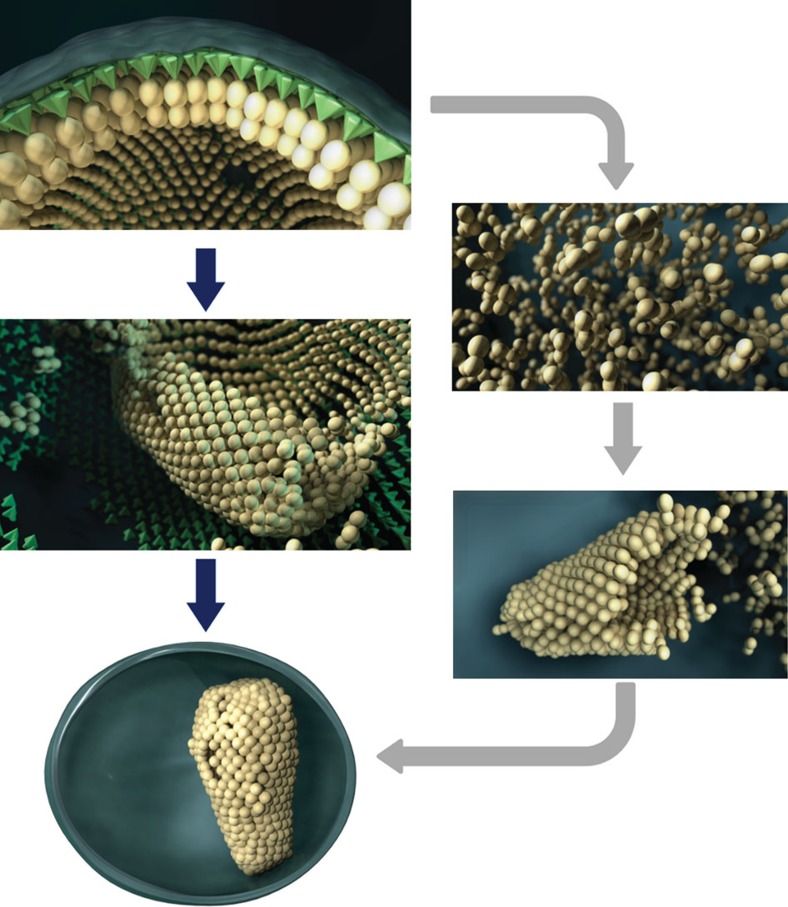
Figure 7. Models for core formation.
(Top) In an immature virion, Gag lattice is arranged beneath the viral membrane. (Right) In the classic model, proteolytic cleavage releases the CA to the viral lumen. CA monomers then nucleate and grow in a diffusion-controlled process, closing off when the opposing membrane is reached. (Left) In our model, CA layer is released by proteolytic cleavage and rolls while transforming to the mature lattice arrangement, until the core is fully formed.