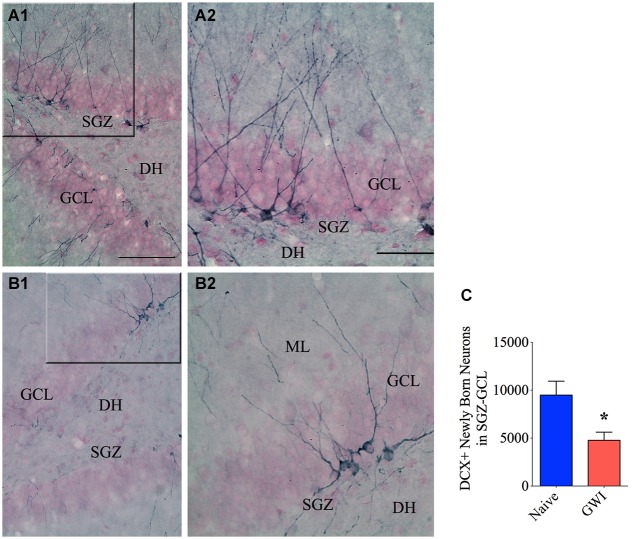
Figure 4.
Exposure to Gulf war illness related (GWIR) chemicals and stress leads to diminished neurogenesis in the hippocampus. Panels (A1) and (B1) illustrate the distribution of doublecortin-positive (DCX+) interneurons in the subgranular zone-granule cell layer (SGZ-GCL) of the DG from an age-matched naive control rat (A1) and a rat that was exposed to Gulf War illness related (GWIR) chemicals and stress 3 months earlier (B1). The panels (A2) and (B2) are magnified views of marked regions from (A1) and (B1) showing the morphology of DCX+ newly born neurons. Scale bar (A1) and (B1) = 100 μm; (A2) and (B2) = 50 μm. DH, dentate hilus; ML, molecular layer. The bar chart (C) compares numbers of newly born (DCX+) neurons in the DG between naive control rats and rats exposed to GWIR-chemicals and stress. *p < 0.05.