Figure 1.
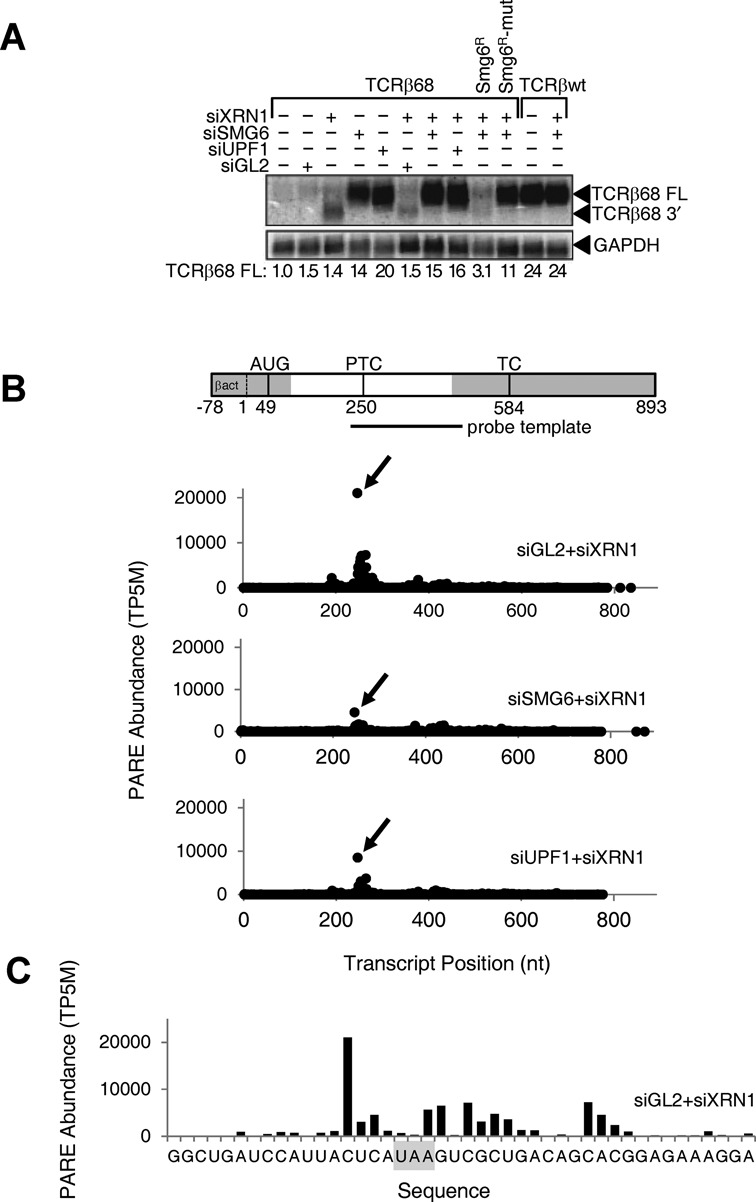
Effect of SMG6 or UPF1 depletion on the concentration of the full-length TCRβ68 transcript and its 3′-terminal SMG6 cleavage product. HeLa cells that expressed a TCRβ68 transcript harboring a PTC at codon 68 (TCRβ68) or a wild-type TCRβ transcript lacking a PTC (TCRβwt) were transfected with siRNAs directed against XRN1, SMG6 or UPF1, or with siGL2 (negative control). Total RNA extracted from these cells was used to prepare PARE libraries. (A) Detection of both a full-length transcript (TCRβ68 FL) and a 3′-terminal decay intermediate (TCRβ68 3′) by northern blot analysis. As a control, some cells were transfected with an siRNA-resistant SMG6 gene (SMG6R) or a catalytically inactive variant thereof (SMG6R-mut). In each case, the concentration of the full-length transcript relative to that in mock-transfected cells was calculated after normalization to GAPDH mRNA (internal standard). (B) D-plots for the TCRβ68 reporter identifying monophosphorylated 5′ ends detected by PARE in cells transfected with siXRN1 and either siGL2, siSMG6 or siUPF1. A map of the TCRβ68 transcript is shown above the D-plots. Alternating gray and white zones indicate exons. AUG, translation initiation codon; PTC, premature termination codon; TC, natural termination codon. Because the 5′-terminal portion of the reporter was derived from the human β-actin gene, TCRβ68-derived PARE sequences there cannot be distinguished from those originating from the endogenous β-actin transcript. Transcript positions represent the distance from the first nucleotide unique to the TCRβ68 reporter. (C) High-resolution D-plot identifying 5′ ends detected by PARE in RNA from cells transfected with siGL2 and siXRN1. Gray rectangle, PTC.
