Figure 1.
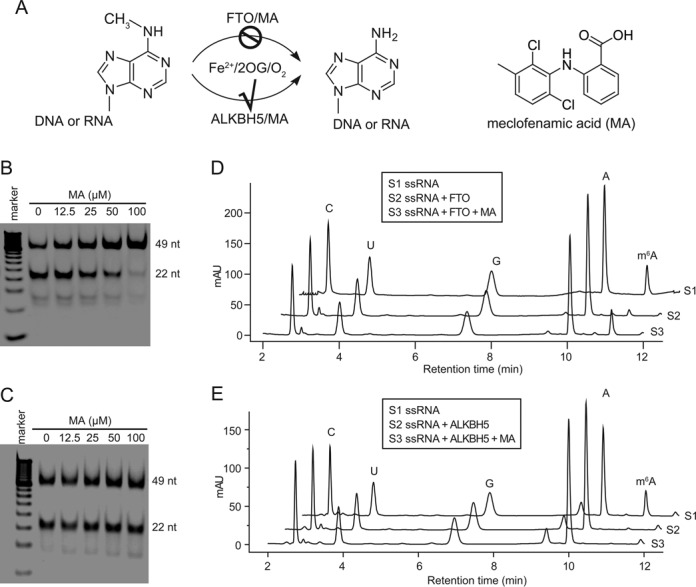
Selective inhibition of m6A demethylases in vitro. (A) Scheme of the reverse of m6A modification in single-stranded nucleic acids by FTO and ALKBH5, respectively. The chemical structure of MA is shown. Our research posed the following question: could the inhibition of FTO be selective and, if so, how? (B) Detection of inhibition of FTO demethylation on ssDNA using the restriction enzyme digestion assay. In PAGE image, the upper band is 49 nt DNA with dm6A incorporation, and the lower band represents the demethylated products after DpnII digestion. MA inhibits FTO demethylation in a dose-response manner. (C) Detection of inhibition of ALKBH5 demethylation on ssDNA using DpnII digestion assay. MA fails to inhibit ALKBH5 demethylation. (D) Shown are HPLC traces of FTO demethylation on m6A in ssRNA in the absence and presence of the inhibitor MA, respectively. (E) Shown are HPLC traces of ALKBH5 demethylation on m6A in ssRNA in the absence and presence of the inhibitor MA, respectively.
