Figure 4.
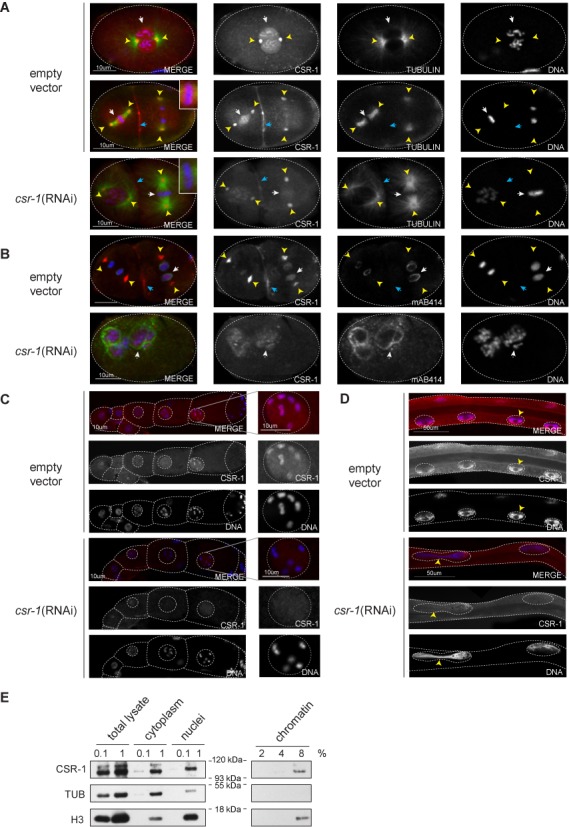
CBR-CSR-1 localizes to chromosomes and centrosomes in multiple stages of C. briggsae development. (A) CBR-CSR-1 localizes to mitotic chromatin (white arrows, prophase and metaphase stages are shown), centrosomes (yellow arrowheads) and the cleavage furrow (blue arrowheads) in C. briggsae embryos. Strain JU1018 was fed dsRNA against empty vector or cbr-csr-1 in (A), (B), (C) and (D). Embryos were stained with DAPI (blue), anti-CEL-CSR-1 (red) and anti-alpha tubulin (green). (B) CBR-CSR-1 shows reduced association with chromatin in anaphase and telophase (white arrow), but remains associated with centrosomes (yellow arrowheads) and the cleavage furrow (blue arrowheads). Embryos were stained with DAPI (blue), anti-CEL-CSR-1 (red) and MAb414, which recognizes nuclear pore complex proteins (green). (C) CBR-CSR-1 localizes to chromatin in C. briggsae oocytes. The germlines of mature adult wild-type and cbr-csr-1 RNAi worms were dissected and stained with DAPI (blue) and anti-CEL-CSR-1 (red). CSR-1 localization to chromatin is reduced in cbr-csr-1 RNAi worms. Single oocyte nuclei are shown as indicated. (D) CBR-CSR-1 localizes to chromatin in C. briggsae gut nuclei. Mature adult wild-type and cbr-csr-1 RNAi worms were stained with DAPI (blue) and anti-CEL-CSR-1 (red). CBR-CSR-1 localization to chromatin is reduced in cbr-csr-1 RNAi worms. Note that cbr-csr-1 RNAi worms display incomplete division of nuclei, consistent with defects in chromosome segregation (arrow heads). (E) Chromatin fractionation assay conducted in C. briggsae embryos confirms the association of CBR-CSR-1 with chromatin (strain AF16). Anti-alpha-tubulin was used as a cytoplasmic control and anti-histone H3 was used as a chromatin control.
