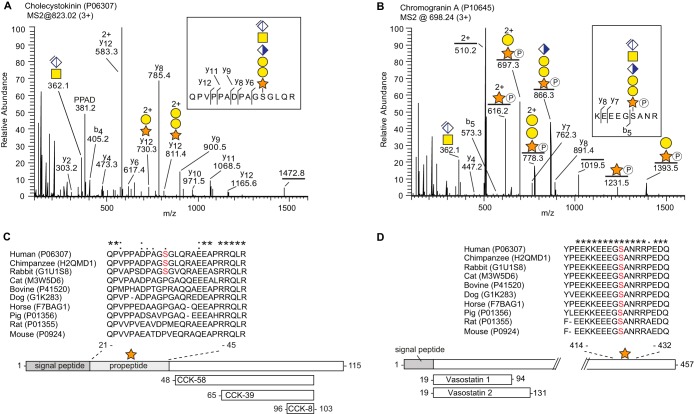
Fig. 3.
Prohormones as a novel class of proteoglycans. A, MS2 fragment spectrum of cholecystokinin (P06307) (m/z 1242.5; 3+). The fragment ion of the peptide backbone (QPVPPADPAGSGLQR, m/z 1472.8; 1+) was identified with an N-terminal glutamine deamination (-NH3). B, MS2 fragment spectrum of CgA (P10645) (m/z 698.2; 3+). C–D, Alignment of the CS-sites in cholecystokinin and CgA of 10 commonly studied mammalian species. The serine residue to which the CS-chain is attached is indicated in red. The comparison shows low similarity for the CS-site in cholecystokinin across species, whereas CgA shows much greater similarity. An asterisk (*) indicates amino acids that are conserved in all species. Homologous amino acid substitutions are indicated with a colon (:) and nonhomologous substitutions with a period (.). Post-translational processing of the prohormones to a few of their known bioactive peptides are shown at the bottom.