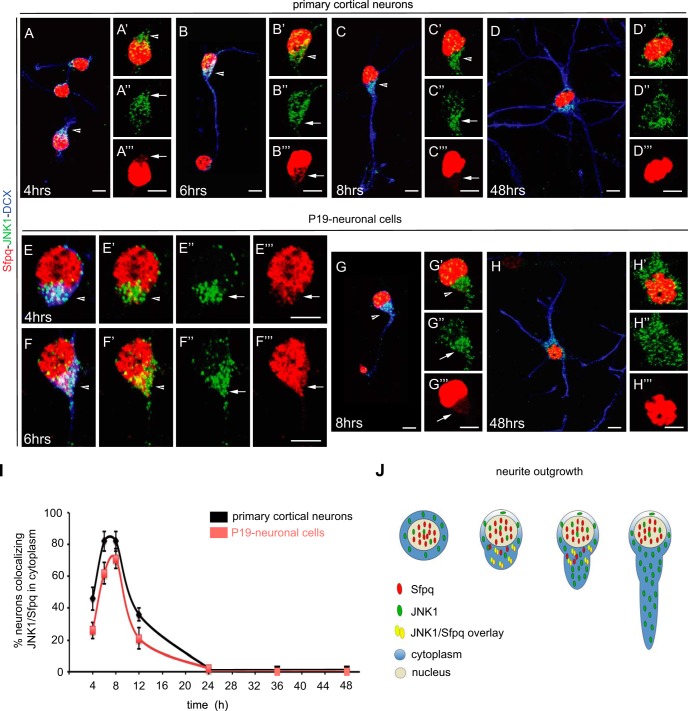
Fig. 7.
Co-localization and cellular distribution of Sfpq and JNK1 in primary cortical neurons and P19 retinoic-acid-treated neuronal cells. Confocal microscopy images of JNK1 (green), Sfpq (red), and the neuronal marker doublecortin (DCX; blue) co-stained in primary cortical (A–D) and P19-diferrentiated neurons (E–H). JNK1 and Sfpq co-localized in the cytosol during the first 12 h after the start of differentiation (see arrows), coinciding with the polarization and outgrowth of primary neurites (A–C, E–F; arrowheads in insets A′–C′ and E′–G′). The cellular distribution of JNK1 (green) during the time course showed that JNK1 was mainly localized in the cytosol (A″–H″). In contrast, Sfpq (red) was localized in the cytosol only during the polarization and outgrowth of primary neurites (A‴–H‴). At later stages, Sfpq was found exclusively in the nucleus (D, H, D‴, and H‴). Scale bar: 5 μm. I, quantification of neurons with co-localization of JNK1 and Sfpq in the cytosol of growing and elongating neurites (n = 150 to 200 neurons per stage). J, schematic representation of the interaction between JNK1 and Sfpq during neurite outgrowth.