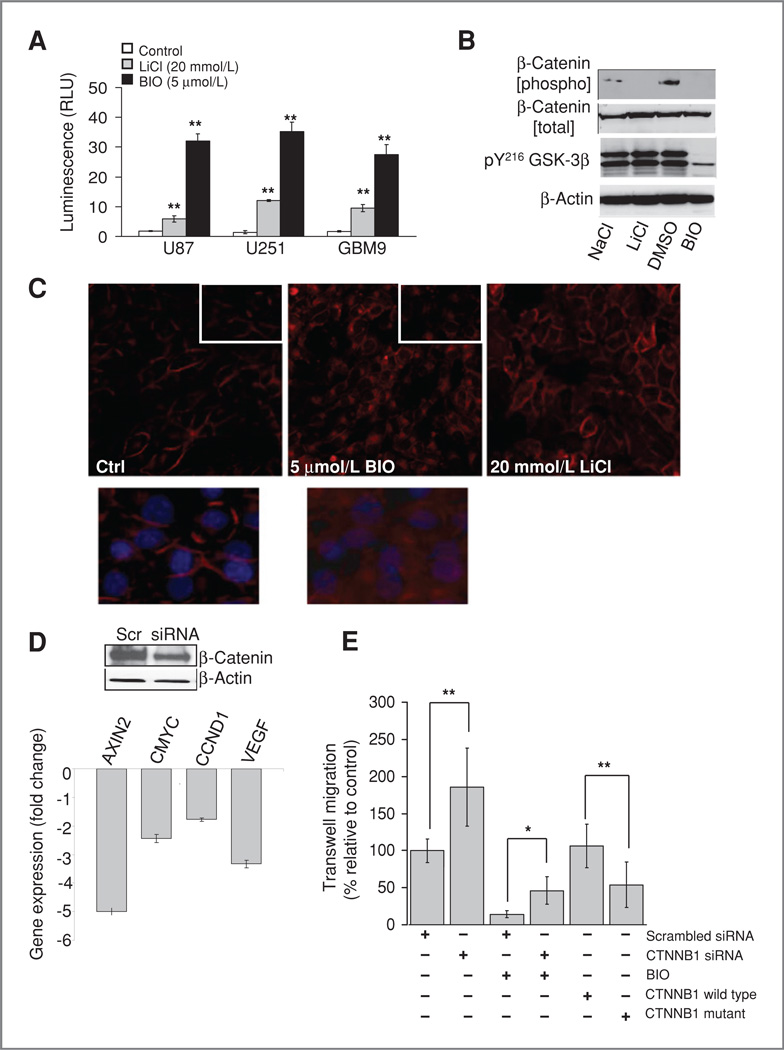
Figure 2.
β-Catenin contributes to the antimigratory effect of BIO. A, β-catenin transcriptional coactivation was measured by using the TOP-flash luciferase reporter vector transfected into glioma cell lines. Luminescence is expressed relative to controls after 24-hour drug treatment. B, phosphorylation of β-catenin (pS33,37, T41) and tyrosine phosphorylation of GSK-3 isoforms was measured by Western blotting 24 hours after treatment with 5 µmol/L BIO or 20 mmol/L LiCl. C, U251 cells were fixed and stained for β-catenin after 1 hour of drug treatment. Inset shows altered localization of β-catenin in BlO-treated cells at high magnification. D, Western blotting showed a reduction of β-catenin levels 48 hours after treatment with siRNA. Quantitative real-time-PCR showed a corresponding decrease in the levels of known β-catenin responsive genes. E, β-catenin levels affect glioma cell migration, β-catenin siRNA treatment leads to increased glioma invasion and partially rescues the effects of BIO in a transwell assay. Conversely overexpression of phospho-mutated β-catenin slows migration.