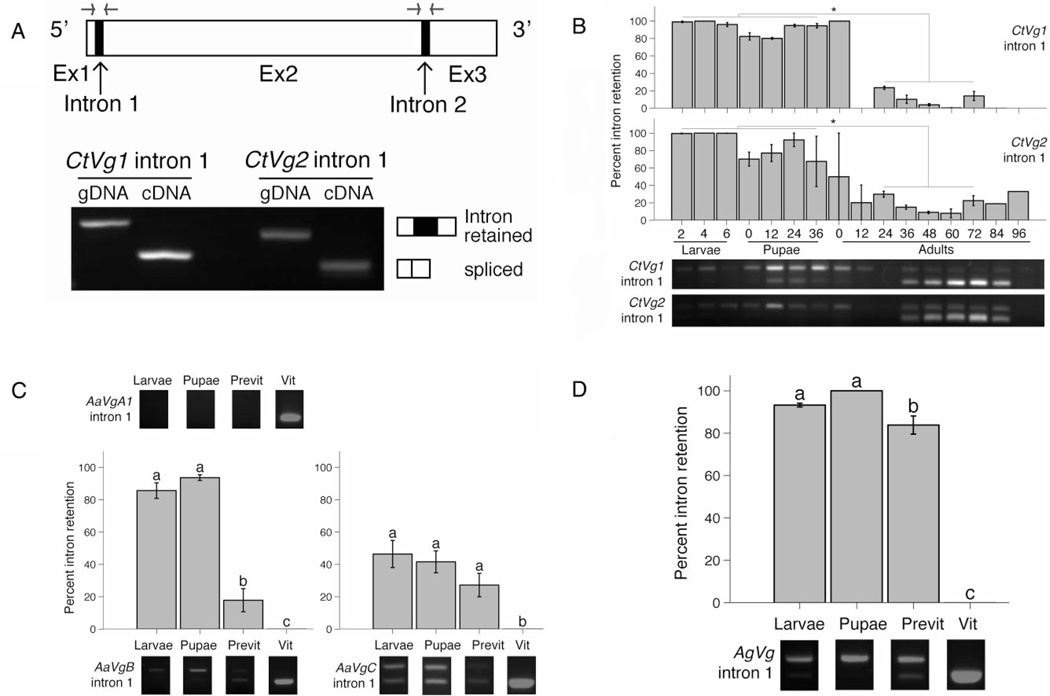
Figure 1.
Vitellogenin transcript expressed during non-reproductive time points in Culex tarsalis, Aedes aegypti and Anopheles gambiae retains the first intron. (A) The conserved structure of mosquito vitellogenin genes consist of three exons as indicated by the open boxes and two short introns as indicated by the filled boxes. The approximate position of the primers that span the intron of interest is illustrated with the forward and reverse arrows. Primers spanning the first intron of C. tarsalis Vg1 and Vg2 genes amplify both intron-containing genomic DNA and spliced cDNA from a vitellogenic female C. tarsalis. (B) Percent C. tarsalis Vg1 and Vg2 transcript that retains the first CtVg intron during larval (days after hatching), pupal (h after pupation) and adult (h after emergence) time points. Data were quantified from reverse transcriptase (RT)-PCR products using intron-spanning primers, CtVg1intron1 and CtVg2intron1. Example gel images are shown below the bar graphs. All the immature time points (larvae and pupae) were found to be significantly different from all the autogenous reproduction time points (defined as 24–72-h-old adults, based on vitellogenin expression profile Provost-Javier et al., 2010) for both CtVg1 intron 1 and CtVg2 intron 1. CtVg1 P < 0.0001, CtVg2 P = 0.0001, anova. Tukey’s Honest Significant Difference (HSD) test was used for pairwise comparisons. *P < 0.05. Expression and intron retention of A. aegypti VgA1, VgB and VgC genes (C) and A. gambiae Vg1–3 genes (D). For (C) and (D), vitellogenin gene expression was investigated by RT-PCR from larvae, female pupae, previtellogenic adult females and vitellogenic adult females. Intron-spanning primers used were: AaVgA1intron1, AaVgBintron1 and AaVgCintron1 for A. aegypti and AgVgintron1 for A. gambiae. Example gel images are shown. The bar graphs represent the mean ± sem. AaVgB P < 0.0001, AaVgC P = 0.0001549, AgVg P < 0.0001, anova. Tukey’s HSD test was used for pairwise comparisons. Stages that are significantly different at P < 0.05 are indicated with different letters. Previt, previtellogenic adult females; Vit, vitellogenic adult females; Ex, exon; gDNA, genomic DNA; cDNA, complementary DNA.