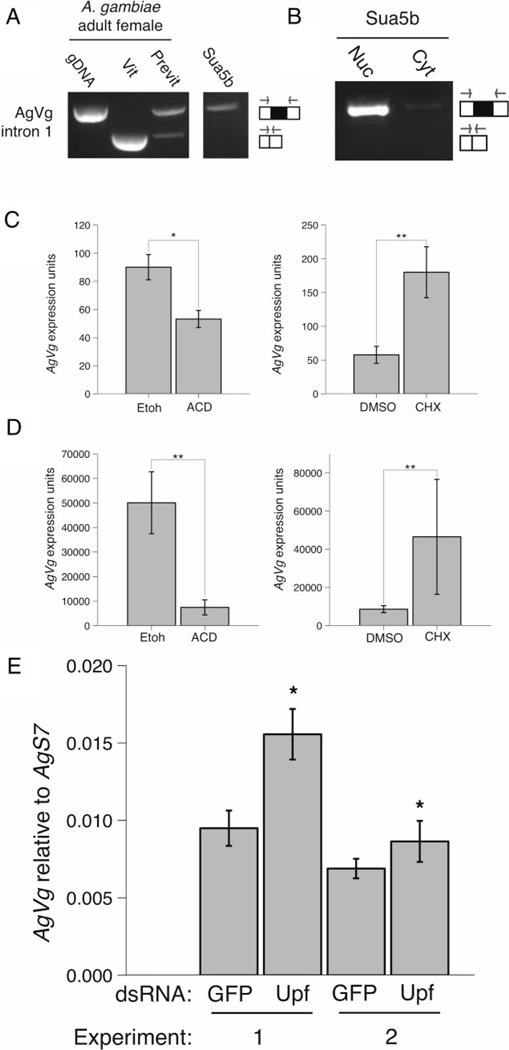
Figure 2.
Intron-retained vitellogenin is degraded by nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD) in Anopheles gambiae cell line, Sua5b, and in A. gambiae fat body culture. Expression of A. gambiae Vg (AgVg) in Sua5b cells by reverse transcriptase PCR performed with intron spanning primers AgVgintron1 on whole cells (A) or cell fractions (B). Adult A. gambiae genomic DNA, vitellogenic and previtellogenic female cDNA serve as controls. AgVg expression for Sua5b cells (C) and previtellogenic A. gambiae in vitro fat body culture (D) treated with a transcriptional inhibitor (actinomycin D) or a translational inhibitor cycloheximide (CHX). Sua5b cells were treated for 8 h and A. gambiae fat bodies were treated for 24 h. AgVg expression (arbitrary units) was measured by quantitative PCR using a standard dilution curve. (E) AgVg expression in Sua5b cells following treatment with double-stranded (ds)RNA against AgUpf1 and AgUpf2 (UPF) or green fluorescent protein (GFP) control over two replicate experiments. There is a significant effect of dsRNA treatment and experimental date, and no significant interaction between dsRNA and date (dsRNA, P = 0.0342, date, P = 0.01831, dsRNA:date, P = 0.15591, Two-way anova). Because of a significant effect of date, graph shows the replicate experiments separately. AgVg expression is shown relative to AgS7. For all, the bar graphs represent the mean ± sem. * P < 0.05; ** P ≤ 0.001, Student’s t-test. t-tests were performed on log-transformed data for Sua5b CHX exp (C, second graph) and fat body ACD exp (D, first graph). gDNA, genomic DNA; Vit, vitellogenic adult female; Previt, previtellogenic adult female; Nuc, nuclear; Cyt, cytoplasmic; ETOH, ethanol; ACD, actinomycin D; DMSO, dimethyl sulphoxide.