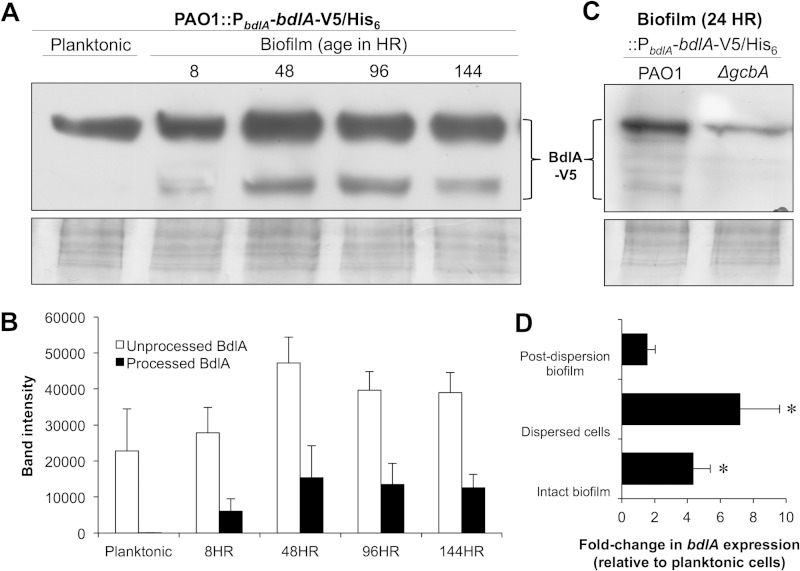
FIG 2.
Cleavage of BdlA is initiated in P. aeruginosa cells following initial attachment to surfaces. (A) Detection of chromosomally encoded, C-terminally V5/His6-tagged BdlA in total cell extracts of P. aeruginosa PAO1 cells grown planktonically or as biofilms for 8, 48, 96, and 144 h by immunoblot analysis using anti-V5 antibody. (B) ImageJ software densitometry analysis of intact BdlA and BdlA cleavage products detected in total cell extracts of P. aeruginosa PAO1 cells grown planktonically or as biofilms for 8, 48, 96, and 144 h. (C) Detection with anti-V5 antibody of chromosomally encoded, C-terminally V5/His6-tagged BdlA in total cell extracts of planktonic or attached (24 h) wild-type PAO1 or ΔgcbA mutant cells. (A, C) Panels below immunoblot images are Coomassie-stained gels after transfer to ensure equal TCE protein loading. (D) Relative transcript abundances of bdlA in P. aeruginosa PAO1 144-h-old biofilm cells (Intact biofilm), cells dispersed from 144-h-old biofilms in response to a changed glutamate concentration in the medium (Dispersed cells), and cells remaining within the biofilm following dispersion (Post-dispersion biofilm). Transcript abundance is reported relative to the abundance in planktonically grown PAO1 cells. (B, D) Error bars represent standard deviations. *, significantly different from expression in planktonically grown PAO1 cells (P < 0.05). All experiments were performed in triplicate, and representative images are shown.