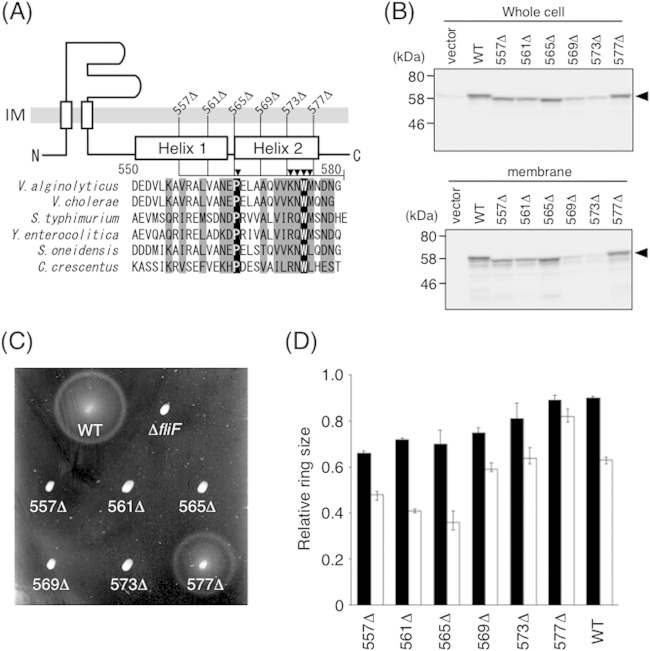
FIG 4.
Function and expression of mutant FliF proteins with a series of C-terminal deletions. (A) Schematic representation of the C-terminal end of V. alginolyticus FliF and sequence alignments of FliF from various species. Segments deleted in this study are shown as lines, and Ala-substituted residues are indicated by closed triangles. Residues shown in black (or gray) boxes are completely (or partially) conserved among these six species. Aligned FliF sequences are from Vibrio alginolyticus, Vibrio cholerae, Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium, Yersinia enterocolitica, Shewanella oneidensis, and Caulobacter crescentus. (B) Expression of mutant FliF proteins with various C-terminal deletions. Whole-cell samples (top) and membrane fractions (bottom) of NMB196 (ΔfliF) cells expressing FliF proteins from the plasmid were prepared from the same cell cultures, analyzed by SDS-PAGE, and immunoblotted with an anti-FliF antibody. Closed triangles show the position of FliF. The vector was pBAD33. (C) Motility of cells on soft-agar plates. NMB196 cells expressing mutant FliF proteins were inoculated on soft-agar plates containing 0.02% arabinose and incubated at 30°C for 6 h. (D) Relative motility ring sizes of the wild-type strain expressing FliF mutants. Motility on soft-agar plates was analyzed for VIO5 cells expressing mutant FliF proteins in the presence of 0.02% (black bars) or 0.2% (white bars) arabinose. Ring sizes were measured and normalized to those of VIO5 cells harboring the vector pTY57. WT, wild type (full-length FliF expressed from plasmid pTY502).