FIG 2.
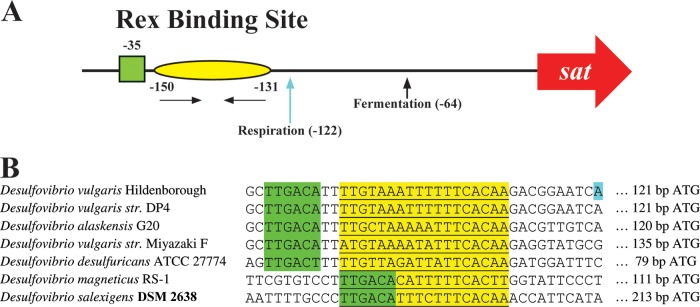
Two transcription start sites (TSSs) for sat identified dependent on growth substrates. Parental and RexDvH mutant strains were grown in medium that would allow for sulfate respiration or pyruvate fermentation. Samples at the early-exponential-growth phase were analyzed for the TSS of sat by 5′-RACE. (A) Schematic representation of sat promoter. The predicted RexDvH-binding site is annotated with a yellow oval with nucleotide positions listed relative to the assumed ATG translational start codon of sat in D. vulgaris Hildenborough. Horizontal arrows denote the half-sites (inverted repeats) within the RexDvH-binding site. The predicted −35 site is indicated by a green box. TSSs are identified with vertical arrows (and positions) for each sample tested. (B) The Rex-binding site (underlined, highlighted in yellow) and the surrounding region is shown for the promoter sequence of sat of Desulfovibrio strains, with the predicted −35 site displayed (TTGACA, highlighted in green). A TSS (respiration) for D. vulgaris Hildenborough is highlighted in blue.
