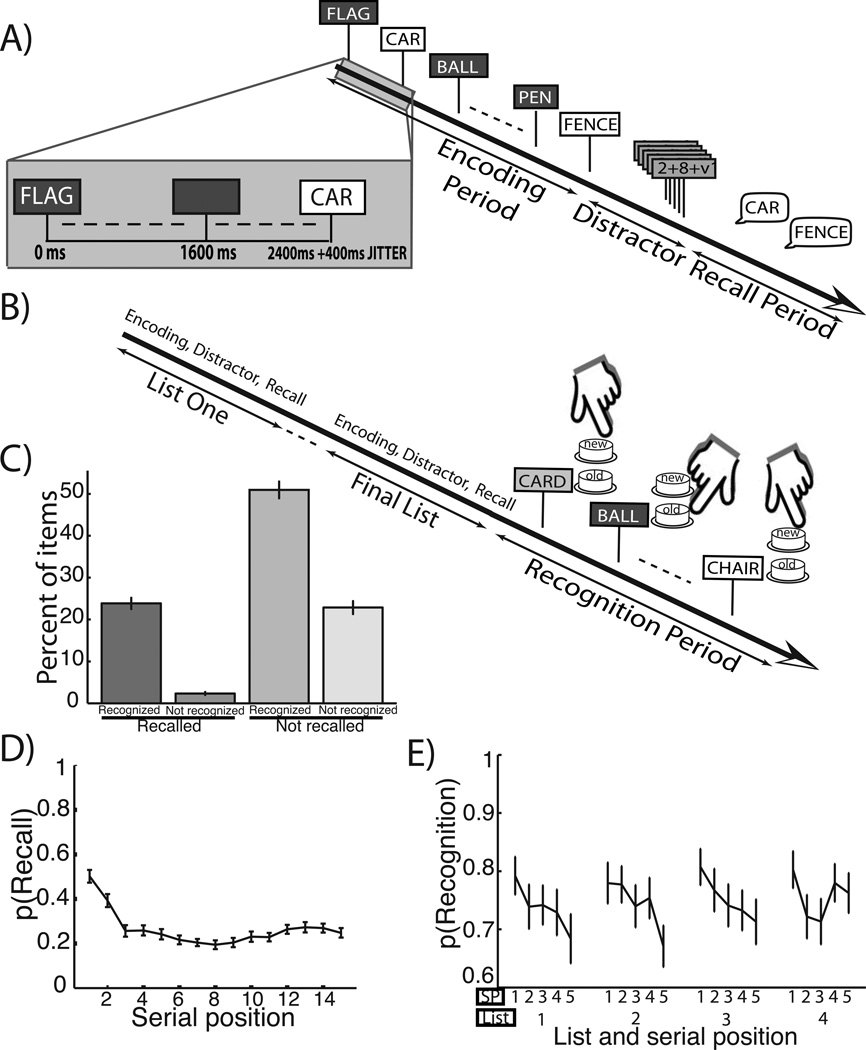
Figure 1.
A. Free–recall task. In this combined task, subjects were first shown a series of 15–word lists followed by a distractor and then asked to recall items from the most recent list. B. Recognition task following free–recall lists. After all recall lists were complete, the subjects were shown 60 targets from the studied items and 60 lures and asked to make a recognition judgment. C. Categorization of words by recall–recognition contingency. Across subject mean and ±1 SEM of the percentage of presented words in one of four categories based on later recall and recognition performance. D. Free–recall serial position curve. Across subject mean and ±1 SEM probability of recall as a function of serial position studied. E. Recognition performance by study list quartile and intra–list serial position quintile. Across subject mean and ±1 SEM probability of recognition as a function of study list quartile and serial position quintle within a list.