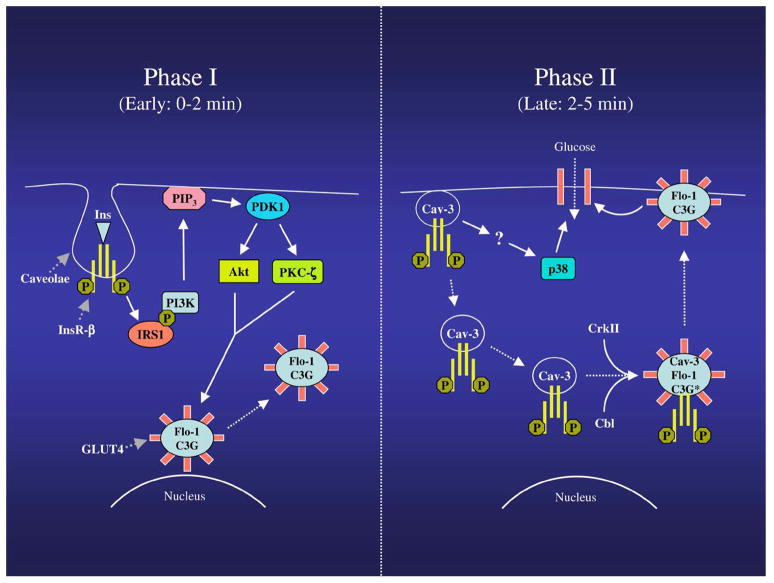
Figure 9.
Schematic diagram summarizing the modulation of GLUT4 translocation by flotillin-1 and caveolin-3. Phase I (0–2 min): Upon insulin stimulation, the insulin receptor, which is localized into caveolar membranes, activates IRS1, which phosphorylates and activates PI3K, with consequent production of PIP3. PIP3 serves as an allosteric regulator of PDK. PDK phosphorylates and activates Akt, as well as PKCζ, which stimulate the movement of flotillin-1/GLUT4-containing domains from a perinuclear compartment toward the plasma membrane. Caveolin-3 expression is necessary for the activation of both PI3K and Akt. Phase II (2–5 min): Caveolin-3-containing domains move from the sarcolemma to the cytoplasm, where they interact with flotillin-1/GLUT4-containing domains. Insulin receptor now moves from caveolin-3-containing domains to flotillin-1/GLUT4-containing domains, where it promotes recruiting of Cbl, and CrkII, as well as activation of C3G (indicated as C3G*). Flotillin-1 expression is necessary for activation of C3G. Activation of flotillin-1/Cbl/C3G-dependent, but PI3K-independent, pathway finalizes the movement of flotillin-1/GLUT4-containing domains to the plasma membrane, where glucose uptake takes place. Caveolin-3 expression is also required for insulin-dependent activation of p38 MAP kinase, which is necessary for glucose uptake.