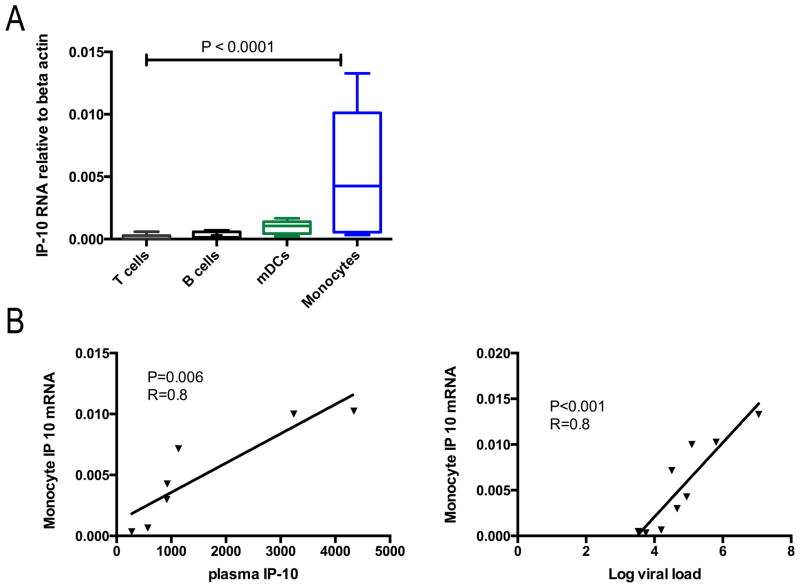
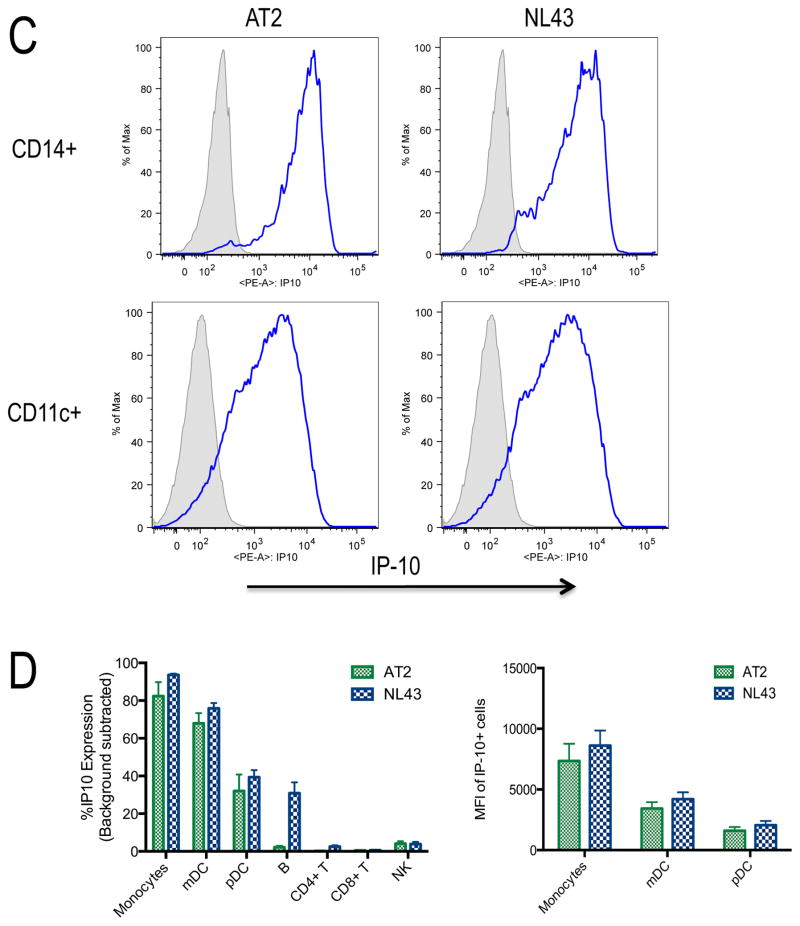
Figure 2. Cellular sources of IP-10.
A) IP-10 mRNA expression in sorted cell populations from individuals with early HIV-1 infection. IP-10 mRNA expression relative to beta actin was determined for each cell population. Box plots show 25th to 75th percentile with whiskers to the minimum and maximum and bisecting line at the median. Data was analyzed with nonparametric analysis of variance using the Friedman’s test with a p<0.0001 across the groups. When controlled for multiple comparisons with the Dunn’s test, the levels differed significantly between T cells and mDCs and monocytes and B cells and Monocytes.
B) Monocyte IP-10 mRNA levels from patient PBMCs are related to both plasma IP-10 level and log viral load. Relative expression of IP-10 mRNA was compared by linear regression to plasma IP-10 levels (left panel) and log viral load (right panel) from matched samples.
C) Assessment of monocyte and mDC production of IP-10 in response to HIV-1. Proportion of monocytes (top row,) and mDCs (second row) that produce IP-10 quantified by intracellular cytokine staining following PBMC stimulation with media (negative, gray shaded histogram) or AT-2 HIV-1 or HIV-1NL43.(blue open histograms). Gating strategies as detailed in the methods section, these plots are representative experiments.
D) In)vitro IP-10 production from different cell types and geometric mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of IP-10 producing cells. Proportion of monocytes, mDCs, pDCs, B cells, CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells, and NK cells that produce IP-10 quantified by intracellular cytokine staining following PBMC stimulation with AT-2 HIV-1 or HIV-1NL43. (left panel). MFI of the IP-10 producing cells from the 3 populations with the most significant production (right panel). Values are reported following background subtraction and represent the average of 5 experiments.