Fig. 2.
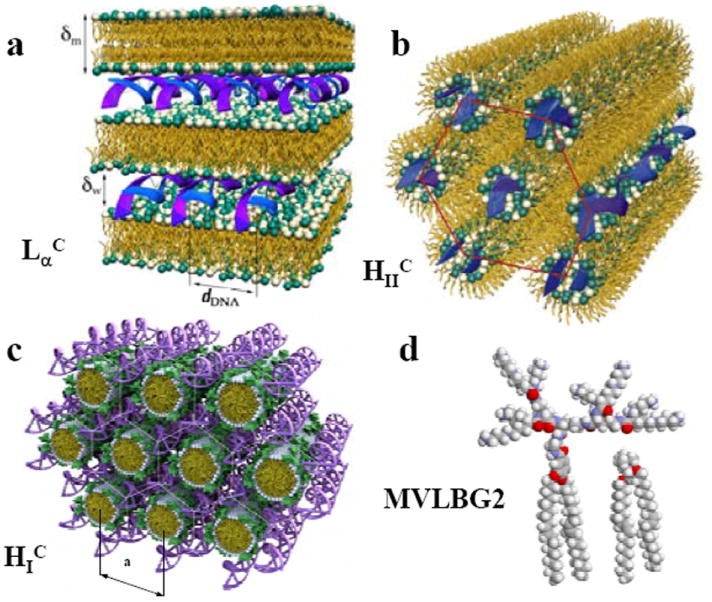
Mixing DNA and cationic liposomes (CLs) results in the spontaneous formation of CL–DNA complexes with equilibrium self-assembled structures. The schematics show the local structure of the interior of CL–DNA complexes on the nanometer scale as derived from synchrotron x-ray diffraction. (a) The lamellar LαC phase of CL–DNA complexes with alternating lipid bilayers and DNA monolayers. (b) The inverted hexagonal HIIC phase of CL–DNA complexes, composed of DNA inserted within inverse lipid tubules which are arranged on a hexagonal lattice. (c) The hexagonal HIC phase of MVLBG2/DOPC–DNA complexes, where the large lipid headgroup of the multivalent lipid MVLBG2 leads to the formation of rod-like lipid micelles arranged on a hexagonal lattice with DNA inserted within the interstices in honeycomb symmetry. (d) Molecular models of dendritic hexadecavalent MVLBG2 (headgroup charge +16 e) and univalent DOTAP (+1 e). Parts (a) and (b) reprinted with permission from references 42 and 43, respectively. Parts (c) and (d) adapted and reprinted with permission from reference 45; copyright 2006 American Chemical Society.
