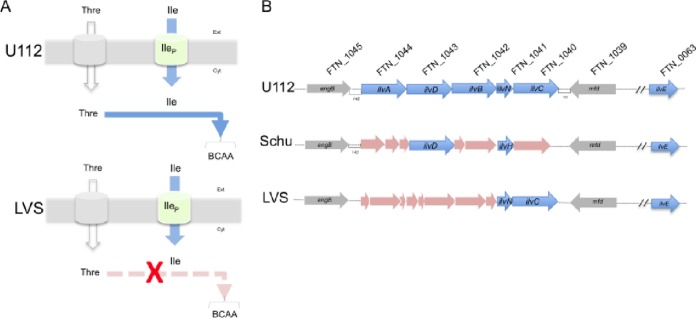
FIG 6.
Isoleucine uptake and the BCAA biosynthetic pathway in Francisella subspecies. (A) Schematic representation of isoleucine (Ile) entry in F. tularensis subsp. novicida and F. tularensis LVS. Isoleucine crosses the bacterial cytoplasmic membrane via the MFS transporter IleP. In F. tularensis subsp. novicida, when threonine is available in the medium, threonine enters the bacterium (via a dedicated transporter) and can serve as a precursor for the biosynthesis of branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) such as isoleucine, leucine, and valine. In contrast, in F. tularensis LVS, isoleucine can only be obtained from the uptake of external isoleucine sources (via IleP and possibly other nonspecific permeases). (B) Schematic representation of the isoleucine-valine operon in F. tularensis subsp. novicida U112 (U112), F. tularensis subsp. tularensis Schu S4 (Schu), and F. tularensis subsp. holarctica LVS (LVS) strains. The intact isoleucine-valine genes are shown in blue, the inactivated genes in LVS and Schu S4 genomes are in pink, the flanking genes (eng and mfd) are in gray.