Figure 2.
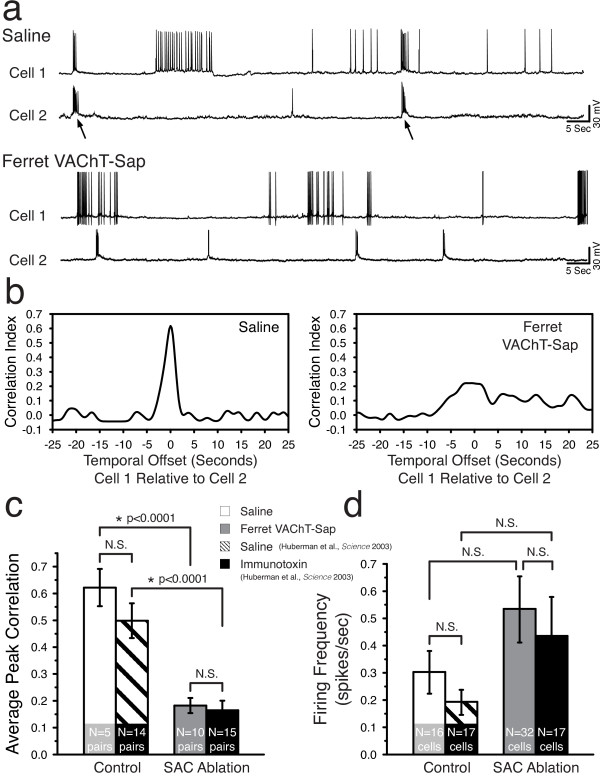
Starburst amacrine cell ablation disrupts correlated spiking between neighboring retinal ganglion cells. Neighboring RGCs in saline control retinae exhibit correlated bursts of action potentials (a, arrows in top traces). Treatment with Ferret VAChT-Sap disrupts correlated firing between neighboring RGC pairs (a, bottom traces). Quantification of the traces in (a) reveals a sharp peak in the cross-correlation function for the saline control pair (b, left panel) which is absent in the Ferret VAChT-Sap-treated RGC pair (b, right panel). This disruption of peak correlation index values following Ferret VAChT-Sap treatment is significant for the entire population of recorded pairs (c, saline in white bar and Ferret VAChT-Sap in grey bar). The values recorded in the current study are not significantly different from those previously reported using a different immunotoxin (c, saline in black striped bar and immunotoxin in black bar; data reanalyzed from Huberman et al.[14]). Treatment with Ferret VAChT-Sap did not significantly impact overall retinal activity levels relative to saline controls (d, saline in white bar and Ferret VAChT-Sap in grey bar), a result reported previously using a different immunotoxin (d, saline in black striped bar and immunotoxin in black bar; data reanalyzed from Huberman et al.[14]). Quantification shows mean ± SEM; statistics reflect two-tailed P values calculated from independent two sample Student’s t-tests. The number of retinae recorded for Ferret VAChT-Sap and saline conditions at P2 was N = 2 and 3, P6 N = 4 and 3, P9 N = 1 and 1, and P10 N = 1 and 1, respectively. NS, not significant.
