Figure 1. INOFs and MSCs promote EOC cell tumourigenicity in vivo.
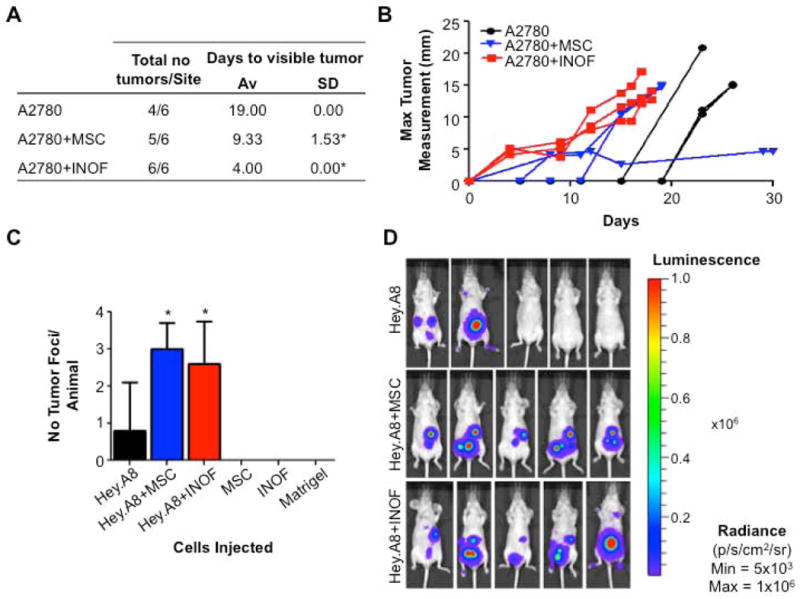
(a) A2780 cells were injected subcutaneously into 3 mice, with 2 injection sites per mouse, this table shows the number of tumours per injection site and the days taken for visible tumour to be detected. Co-injection of stromal cells was associated with a significant reduction in the time taken for palpable tumours to develop. (b) Measurement of maximum tumour diameter in each mouse. (c) In intraperitoneal xenografts, co-injection with stromal cells increases the number of tumour foci detectable at day 10. (d) Live animal Xenogen imaging. Tumours are detected in 2/5 animals that receive 3×106 Hey.A8luc cells alone. Co-injection with stromal cells results in tumour formation in 100% of animals, four animals shown per group. * P>0.05, two-tailed paired Student's T-test, α=0.05, compared to EOC cells injected alone. Error bars = s.d. Animals were examined post-mortem and tumor presence confirmed by macroscopic inspection and histological examination of the lesions. Tumor foci were absent in control mice injected with MSCs, INOFs or Matrigel alone.
