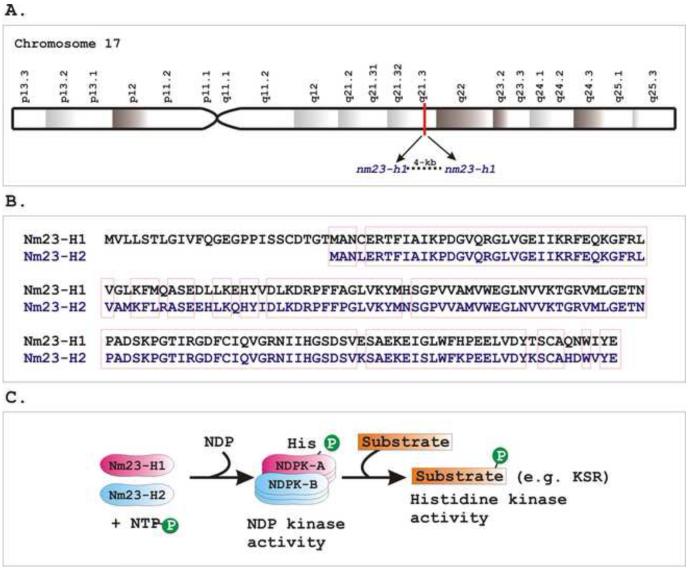
Figure 1. Nm23-H1 and -H2 represent the two best studied proteins of the human Nm23 family.
A) Both nm23-H1 and nm23-H2 mapped 4 kb apart at position q21.3 on chromosome 17. B) Nm23-H1 and Nm23-H2 share approximately 90% amino acids sequence homology. Sequence alignment was generated by a multiple sequence alignment program, ClustalW (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/FTP/). Red boxes depict similar amino acid residues. C) Nm23-H1 and -H2 encode A and B subunits, respectively, of nucleoside diphosphate kinase (NDPK) enzyme, which transfers the terminal phosphates from a nucleoside triphosphate (NTP) to nucleoside diphosphate (NDP). They form either homo- or hetero-hexamers of an active NDPK enzyme complex. Subsequently Nm23 transfers the phosphate moiety to another substrate protein. For example, the kinase suppressor of Ras oncoprotein (KSR) is a substrate for the histidine kinase activity of Nm23-H1.