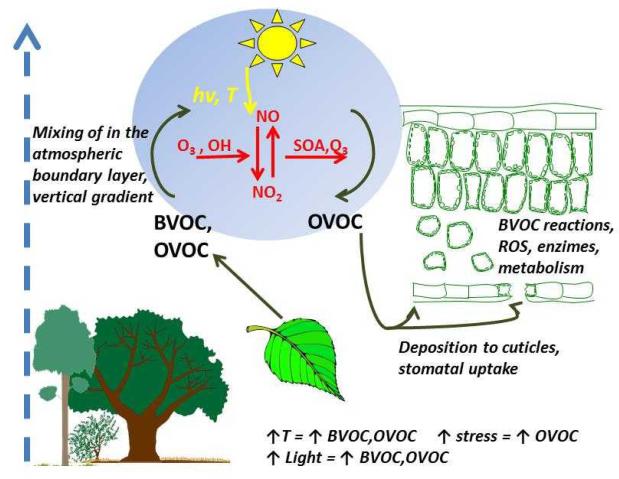
Figure 3.
Biogenic volatile (BVOC) and oxygenated volatile (OVOC) atmosphere-ecosystem exchange dynamics. The vegetation/atmosphere exchange is highly dynamic and is driven by BVOC and OVOC formation in the leaves, BVOC emission, oxidation inside the leaves and in the atmosphere and by foliar uptake (dry deposition). Primary OVOC can be produced by plants by primary metabolic reactions. Secondary OVOC can be produced by oxidation of non-oxygenated volatiles, and in atmospheric reactions involving primary plant/produced compounds. This dynamic exchange further leads to important feedbacks between secondary organic aerosol formation and atmospheric reactivity that alters the concentrations of volatiles in the atmosphere (e.g., Kulmala et al. 2013 for the discussion of the feedbacks).