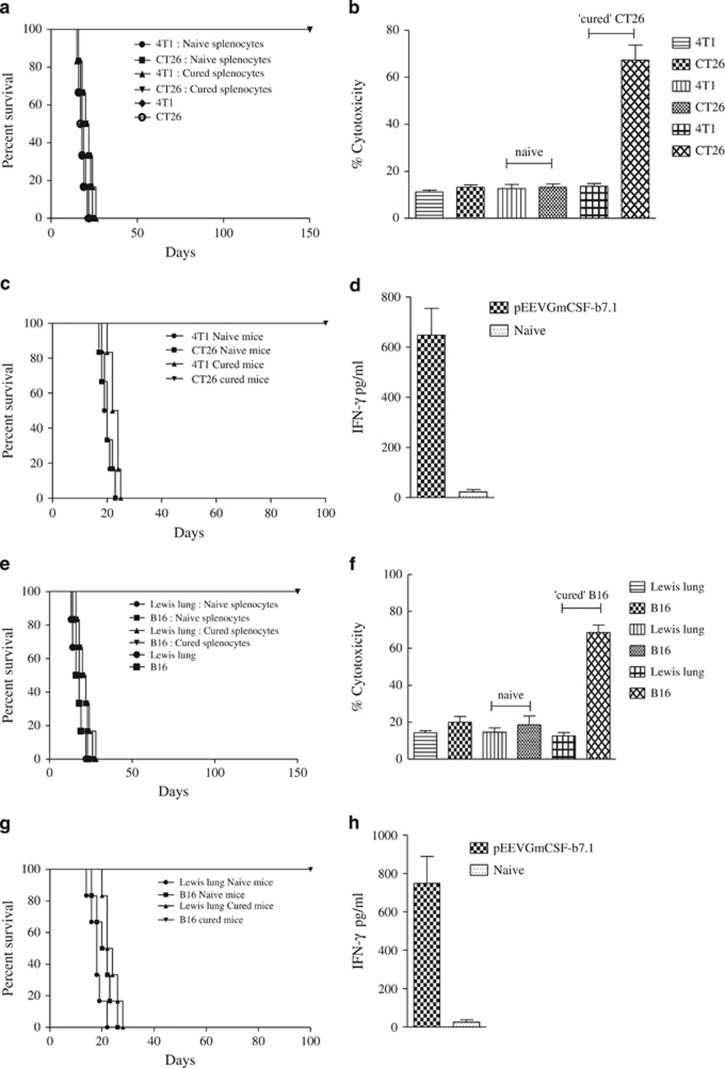
Figure 5.
Tumour protection, cytotoxicity and immune memory. (a) Tumour protection was observed in the pEEVGmCSF-b7.1-treated CT26 mice when challenged (subcutaneously) with 1 × 106 tumour cells (Balb/C n=6 per group) in the left flanks. ‘Cured' and naive mice were challenged with CT26 and 4T1 tumour cells. These mice were monitored for tumour development. One hundred per cent survival was observed in the CT26 cured mice challenged with CT26. All other groups were killed because of tumour burden by day 25. Similar results were obtained in two independent experiments. (b) Augmentation of the in vitro cytolytic activities of the spleen after pEEVGmCSF-b7.1 treatment of CT26 tumours; the specific cytotoxicity was greatest at an effector:target ratio of 50:1 after 48 h incubation. Groups included CT26, 4T1 cells and naive and ‘CT26 cured' splenocytes incubated with CT26 and 4T1 cells, respectively. The highest cytotoxicity was observed in the CT26 cells incubated with splenocytes obtained from ‘CT26 cure' mice treated with pEEVGmCSF-b7.1. The data shown represent one of two separate experiments with similar results (n=6 per group). (c) Adoptive transfer of lymphocytes of CT26 study. Mice (n=6) received subcutaneous injections of a mixture of mice receiving CT26 cells and splenocytes either from cured or naive mice, a mixture of 4T1 cells and splenocytes either from cured or naive mice and CT26 cells only or 4T1 cells only. All mice receiving mixtures of CT26 cells and splenocytes either from cured or pEEVGmCSF-b7.1 treatment survived up to 150 days, whereas tumours developed in all animals within the other groups. (d) Interferon-γ production measured from supernatents obtained from stimulated splenocytes collected from rechallenged—adoptive transfer survivors (50 days post-treatment) and naive animals and IFN-γ was measured. High levels of IFN-γ were produced by pEEVGmCSF-b7.1-treated mice. The y axis represents the concentration of IFN-γ in pg ml−1 of the supernatant from the stimulated splenocytes. Error bars show s.d. from six animals. (e) Tumour protection was observed in the pEEVGmCSF-b7.1-treated B16F10 mice when challenged (subcutaneously) with 2 × 105 tumour cells (C57BL/6J n=6 per group) in the left flanks. ‘Cured' and naive mice were challenged with B16F10 and Lewis lung tumour cells. These mice were observed for tumour development. One hundred per cent survival was observed in the B16F10 cured mice challenged with B16F10. All other groups were killed because of tumour burden by day 28. Similar results were obtained in two independent experiments. (f) Augmentation of the in vitro cytolytic activities of the spleen after pEEVGmCSF-b7.1 treatment of B16F10 tumours; the specific cytotoxicity was greatest at an effector:target ratio of 50:1 after 48 h incubation. Groups included B16F10, Lewis lung cells and nive and ‘B16F10 cured' splenocytes incubated with B16F10 and Lewis lung cells, respectively. The highest cytotoxicity was observed in the B16F10 cells incubated with splenocytes obtained from ‘B16F10 cure' mice treated with pEEVGmCSF-b7.1. The data shown represent one of two separate experiments with similar results (n=6 per group). (g) Adoptive transfer of lymphocytes of B16F10 study. Mice (n=6) received subcutaneously injections of a mixture of B16F10 cells and splenocytes either from cured or naive mice, a mixture of Lewis lung cells and splenocytes either from cured or naive mice, B16F10 cells only or Lewis lung cells only. All mice receiving mixtures of B16F10 cells and splenocytes either from cured from pEEVGmCSF-b7.1 treatment survived up to 150 days, whereas tumours developed in all animals within the other groups. (h) Interferon-γ production measured from supernatants obtained from stimulated splenocytes collected from rechallenged—adoptive transfer survivors (~50 days post-treatment) and naive animals and IFN-γ was measured. High levels of IFN-γ were produced by pEEVGmCSF-b7.1-treated mice. The y-axis represents the concentration of IFN-γ in pg ml−1 of the supernatant from the stimulated splenocytes. Error bars show s.d. from six animals.