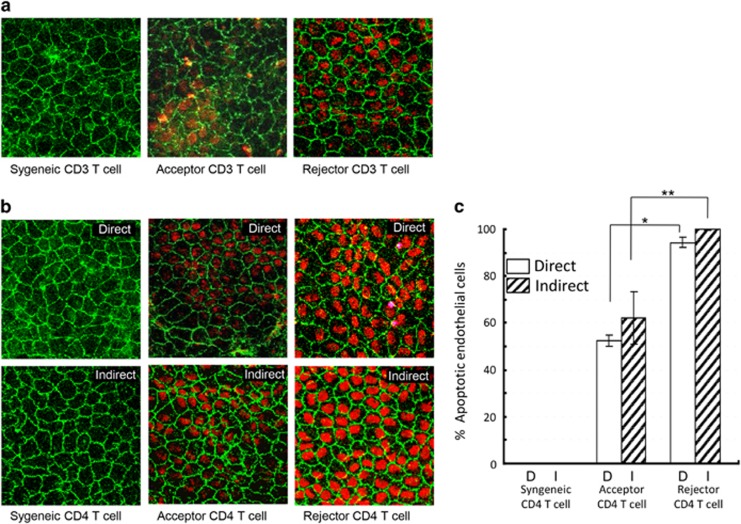
Figure 1.
Effect of alloimmunity on CECs. (a) Representative confocal micrographs showing naive C57BL/6 (graft donor) corneal cups incubated with allogeneic (Balb/c, graft recipients) CD3+ T cells isolated from the draining lymph nodes of syngeneically grafted recipients, allograft acceptors, or allograft rejectors at week 3 after transplantation. After 48 h of incubation, corneas were stained for zonula occluden-1 (ZO-1) (green) and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling assay (TUNEL) (red) to visualize endothelial cell-to-cell junctions and apoptotic cells, respectively (magnification × 40). (b) Representative confocal micrographs showing naive C57BL/6 (graft donor) corneal cups incubated directly or indirectly (using transwells of 1-μm pore size) with CD4+ T cells isolated from the draining lymph nodes of syngeneically grafted recipients, allograft acceptors, or allograft rejectors at week 3 after transplantation. CD4+ T cells induced apoptosis of CECs in a contact-dependent (direct; upper panel) or contact-independent (indirect; lower panel) manner. (c) Bar diagram showing the percentages of apoptotic (TUNEL-positive) CECs in a contact-dependent (direct) or contact-independent (indirect) manner incubated ex vivo with allogeneic CD4+ T cells of the different graft recipient groups. Data are presented as mean±SEM. (*P=0.0002; **P=0.004). Each group consists of n=6 mice and data from one out of three independent experiments is shown.