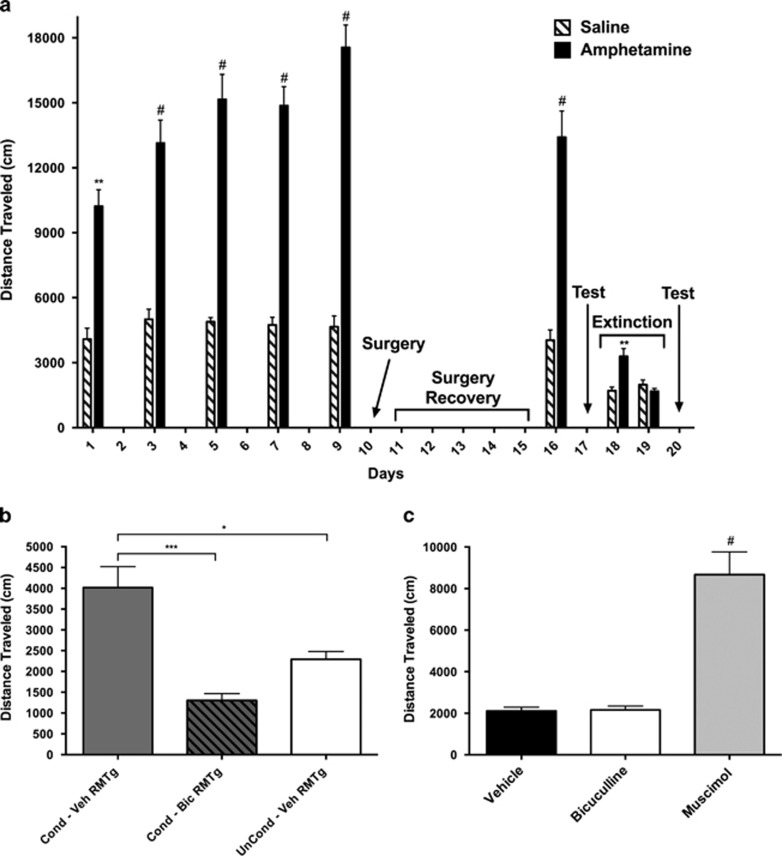
Figure 3.
(a) Diagram depicting the conditioned locomotion experimental protocol. Amphetamine-conditioned and unconditioned rats were generated by administering i.p. injections of either D-amphetamine (1 mg/kg) or an equivalent volume of saline and placing them in activity monitors for 60 min every other day for five sessions (days 1, 3, 5, 7, and 9). One day after the final conditioning session, cannulae were surgically implanted (day 10, ‘Surgery'), and after 1 week of recovery (Days 11–15, ‘Surgery Recovery') the rats received an additional amphetamine-conditioning session on Day 16 and were tested the following day (Day 17, ‘Test'). During the next 2 days, the amphetamine conditioning was extinguished until distance traveled for 20 min was no different between groups (Days 18–19, ‘Extinction') then on separate days, beginning on day 20, the rats received RMTg infusions of saline, bicuculline, and muscimol and were again tested (Day 20, ‘Test'). Data were tested with a two-way ANOVA and post hoc Sidak's multiple comparison's test. #p<0.0001 and **p<0.01 relative to the saline-injected control group. (b) Data from the testing done on day 17. Rats in the unconditioned group (n=5) were given bilateral infusions in the RMTg of vehicle (0.125 μl), and an i.p. injection of saline, and placed in the activity monitors. Amphetamine-conditioned rats were split into two groups, of which rats of one received bilateral infusions of vehicle (n=7) and of the other, bicuculline (n=5), into the RMTg, after which all were given i.p. saline and placed in the monitors. Distance traveled was recorded during 20 min. (c) Distance traveled after infusions of saline, bicuculline, or muscimol into the RMTg on separate days, beginning on Day 20. Total distance traveled was recorded for 20 min. Data in panels (b and c) were tested with a one-way ANOVA and post hoc Tukey's multiple comparisons test. In panel (b): *p<0.05 and ***p<0.001. In panel (c): #p<0.0001 relative to vehicle.