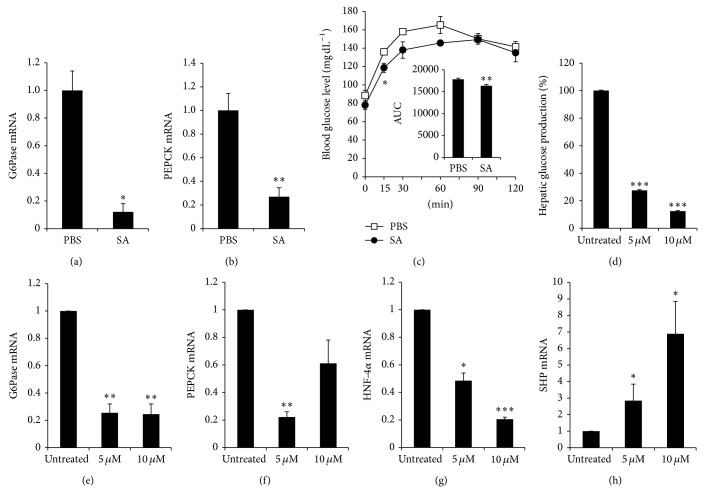
Figure 4.
SA suppressed gluconeogenic gene expression in the liver of SA-treated db/db mice and inhibited glucose production and gluconeogenic gene expression in hepatocytes. Diabetic db/db mice were orally intubated with SA (10 mg kg−1 body weight/day) or PBS. Eight weeks later, the liver tissue was removed. The mRNA expression of (a) G6Pase and (b) PEPCK was analyzed by RT-qPCR and normalized by cyclophilin expression. The fold change was calculated as a ratio of the expression level in PBS-treated diabetic db/db mice. * P < 0.005, ** P < 0.0001 compared with PBS-treated group (n = 4–9/group). (c) For pyruvate tolerance tests, C57BL/6 mice were orally intubated with SA (10 mg kg−1 body weight) or PBS and then fasted overnight. Fifteen hours after SA oral intubation, mice were injected i.p. with 1 g kg−1 body weight of sodium pyruvate in PBS, and blood glucose levels were measured at 0, 15, 30, 60, 90, and 120 min after pyruvate injection (n = 3-4 per group). The area under the curve (AUC) was calculated. * P < 0.05 and ** P < 0.01, compared with PBS-treated mice. (d) Primary hepatocytes from C57BL/6 mice were incubated with 5 or 10 μM SA for 48 h and cultured in glucose-free DMEM supplemented with 20 mM sodium lactate and 2 mM sodium pyruvate for 2 h. Glucose production in media was measured and normalized by the amount of total protein. Relative glucose production was calculated as a percent of glucose production from untreated hepatocytes. Primary hepatocytes from C57BL/6 mice were incubated with 5 or 10 μM SA for 24 h, and the expression of (e) G6Pase, (f) PEPCK, (g) HNF-4α, and (h) SHP mRNA was analyzed by RT-qPCR, with values normalized to cyclophilin expression. The fold change was calculated as ratio of the expression in untreated hepatocytes. Data are mean ± SE from three to four independent experiments. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, and *** P < 0.001 compared with untreated hepatocytes.