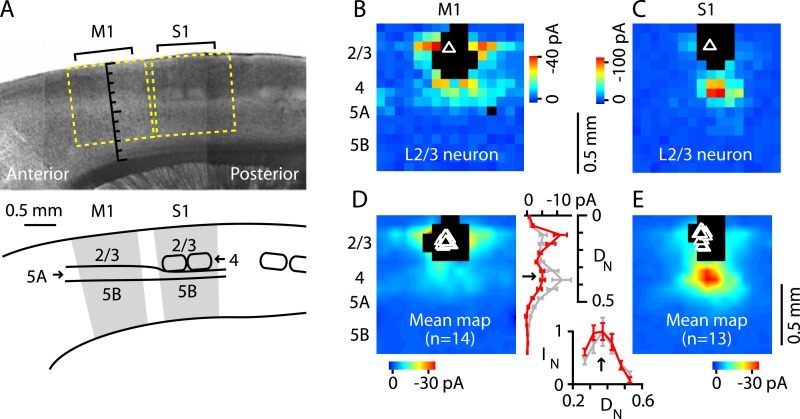
Figure 4. Excitatory output from M1-L4 neurons to L2/3.
(A) Top: bright-field image of a parasagittal slice containing motor (M1) and somatosensory (S1) cortex. In S1, L4 barrels are easily discernable, but are absent from M1, where L5A (lighter-appearing laminar zone) appears wider than in S1. Graduated scale indicates cortical depth in normalized units, from the pia (0) to the white matter (1). Yellow boxes indicate placement of photostimulation grid for mapping inputs to L2/3 neurons in both cortical areas. Bottom: Schematic indicating the major areas and layers of interest in the image. (B) Example of a synaptic input map recorded in a L2/3 neuron in M1. Grid spacing was set to 75 µm, the top of the grid was flush with the pial surface, and the grid was horizontally centered over the soma (triangle). Cortical layers indicated to the left, with the location of the L3/5A border (as observed under bright-field) marked by a horizontal line. Inputs arise from both this L4-like laminar zone and the lateral sites in L2/3. Photosimulation sites where the postsynaptic neuron's dendrites were directly stimulated were excluded from analysis and are shown as black pixels. (C) Example of a synaptic input map recorded in a L2/3 neuron in S1. Same mapping parameters as in B. The input pattern is similar to that of the M1 example shown in B, but with weaker L2/3 and stronger ascending input from the subjacent region corresponding to the L4 barrel layer. (D): Mean input map for M1 neurons (n = 14). The laminar profile (plotted to the right of the map; red, M1; gray, S1) shows a peak at the level of the L3/5A border (black arrow), ∼0.5 mm deep, corresponding to ∼1/3 of the normalized cortical depth (DN) in both M1 and S1. The bottom plot shows the L4 region of the same plot, with the input profiles normalized (IN) to their peak values in L4 (arrow); the scaled M1 profile closely resembles the S1 profile. (E): Mean input map for S1 neurons (n = 13).