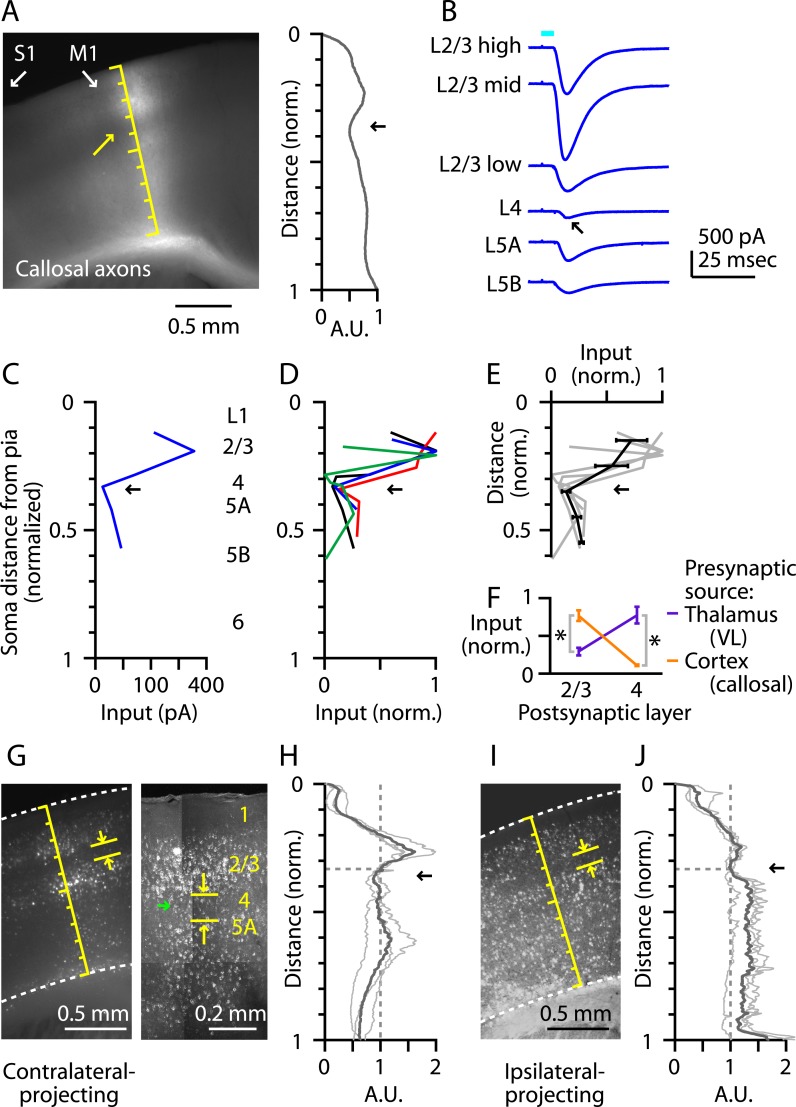
Figure 6. M1-L4 neurons receive and send relatively little long-range corticocortical input.
(A) Epifluorescence image of coronal slice containing M1, showing laminar pattern of labeled interhemispheric corticocortical axons following injection of AAV carrying ChR2 and GFP in the contralateral M1. Scale shows normalized cortical distance. Arrow indicates laminar zone of labeling where weakest photostimulation-evoked electrophysiological responses were also detected. Plot to the right shows laminar profile of fluorescence intensity, in arbitrary units (A.U.), across layers (normalized distance from pia). (B) Responses recorded (sequentially) in vitro in multiple M1 neurons in different layers (as indicated) to photostimulation of ChR2-labeled axons of contralateral M1 neurons infected with AAV-ChR2. (C) Response amplitudes of the same neurons plotted as a function of laminar location, providing a laminar profile of contralateral M1 input to M1 neurons. The profile exhibits a dip in the upper ∼1/3 of the cortex (corresponding to L4) (arrow). (D) The laminar profiles were obtained from multiple slices (n = 4). Profiles show a dip ∼1/3 deep in the cortex (in normalized coordinates). (E) Average laminar profile (black; bars: s.e.m.), calculated by binning the data for each profile (bin width: 1/10 of the normalized cortical depth), averaging within each bin, and then averaging across all profiles. The individual profiles are also shown (gray). (F) Comparison of input from callosal axons (from contralateral M1; n = 4 slices) vs thalamic axons (from VL; n = 6 slices), recorded in postsynaptic L2/3 and L4 neurons in M1 (*p < 0.01, rank-sum test). For each slice, values within each laminar zone (in units of normalized cortical depth: L2/3, 0.1 to 0.25; L4, 0.29 to 0.37) were averaged to obtain a single value per profile; these were averaged and plotted with error bars representing the s.e.m. (G) Representative epifluorescence image (left) showing gap (marked by yellow arrows) at the level of L4 (∼1/3 deep in the cortex, in normalized distance units) in the retrograde labeling of M1 neurons following injection of retrograde tracers in contralateral M1. Two-photon microscopic image (right) showing the same labeling pattern at a higher resolution (different animal). Some neurons within the ‘gap’ are labeled with the retrograde tracer (green arrow). (H) Laminar profiles of fluorescence intensity of M1 neurons projecting to contralateral M1. Each trace represents the average profile for one animal, obtained by averaging several M1-containing slices. For display, the profiles were normalized to the value in L4 (specifically, the value at a normalized cortical depth of 1/3). The bold line is the average of three animals. There is a reduction in labeling intensity in the L4 region (arrow). (I) Representative epifluorescence image showing gap at the level of L4 in the retrograde labeling of M1 neurons following injection of retrograde tracers into ipsilateral M2, S1, and S2. (J) Laminar profiles of retrograde labeling pattern for ipsilateral injections. Average traces were calculated as in Panel G. The average (bold line) of three animals shows a zone of reduced labeling observed ∼1/3 deep in the cortex, corresponding to L4 (arrow).