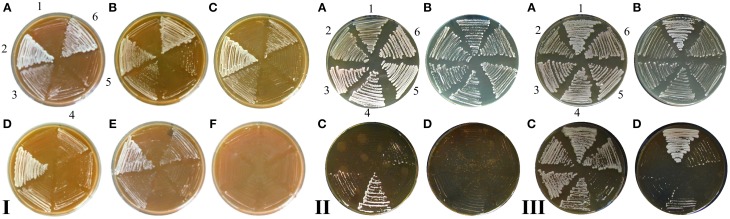
Figure 7.
Cox1 gene as the main determinant of xenonucleo-mitochondrial (in)compatibility. (I) Growth of non-adapted S. cerevisiae cybrids with mitochondrial genomes from S. paradoxus CBS 7400 (A); S. paradoxus CBS 2908 (B); S. mikatae CBS 8839 (C); S. kudriavzevii CBS 8840 (D); S. bayanus CBS 380 (E); MCC109 ρ0 Strain (negative control) (F); after mating to different mit− strains: (1) MD79 (mit− in cox1), (2) akar170 (mit− in trnAsp), (3) M1301 (mit− in cob), (4) AD1 (mit− in cox1); (5) 5B (mit− in cox1); (6) K2145 (mit− in cox2). Cultivated on YPGE plates for 4 days at 30°C. Growth of non-adapted cybrids after the mating with S. cerevisiae DBY 747 ρ0 (II) and S. cerevisiae DBY 747 ρ− containing intronless cox1 gene (III) mit− strain 2612 (positive control) (1); S. cerevisiae cybrids with mitochondrial genomes from: S. paradoxus CBS 7400 (2); S. paradoxus CBS 2908 (3); S. kudriavzevii CBS 8840 (4); S. mikatae CBS 8839 (5); S. paradoxus CBS 7400 (6). Plates (A) YPD 30°C, (B) YPD 37°C, (C) YPGE 30°C, (D) YPGE 37°C. Cultivation 4 days.