Figure 1.
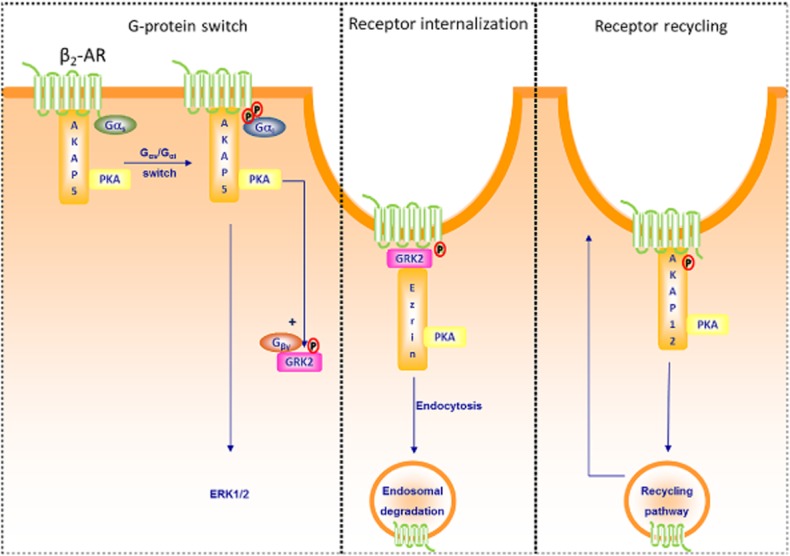
Members of the AKAP family and the function of the β2-adrenoceptor (β2–AR). Left: AKAP5 has been shown to constitutively associate with the β2-adrenoceptor receptor (Fraser et al., 2000; Lynch et al., 2005; Chen and Malbon, 2013). Upon β2-adrenoceptor activation, AKAP5-bound PKA phosphorylates the receptor, facilitates the switch of Gs to Gi and thereby permits signalling to ERK (Fraser et al., 2000; Lynch et al., 2005). In addition, AKAP5-bound PKA phosphorylates GRK2, enhances the affinity of GRK2 for Gβγ subunits and subsequent interaction with the β2-adrenoceptor (Cong et al., 2001). Middle: Receptor-bound GRK2 has the ability to interact with Ezrin (AKAP78), the latter known to be required for the internalization of the β2-adrenoceptor (Cant and Pitcher, 2005). Right: β2-adrenoceptor activation leads also to phosphorylation of AKAP12 via bound PKA and increases the association of AKAP12 with the β2-adrenoceptor receptor, a process known to be essential for the recycling of the β2-adrenoceptor (Shih et al., 1999; Tao et al., 2003).
