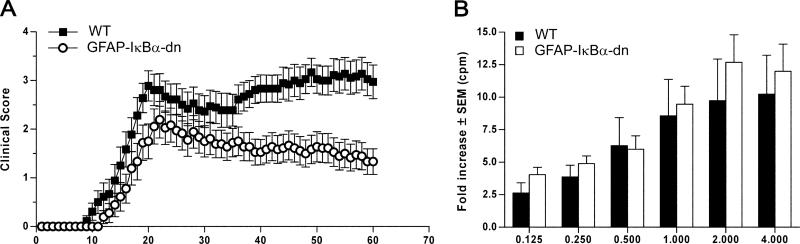
FIGURE 1.
Inhibition of astroglial NF-κB improves functional outcome following EAE. A, Clinical course of MOG35–55-induced EAE in WT and GFAP-IκBα-dn mice. EAE symptoms were scored daily for 60 days, as described in Materials and Methods. Results are expressed as the daily mean clinical score ± SEM of 18 animals/group from two independent experiments. Curves are significantly different (p < 0.0001, Mann-Whitney U test). B, Cell proliferation assay on T cells isolated from WT and GFAP-IκBα-dn mice undergoing active EAE 2 wk after immunization. Following exposure to increasing MOG concentrations, cells were pulsed with [3H]thymidine, and proliferation was assessed in cpm of incorporated tritiated thymidine. Results are expressed as mean fold increase incorporation relative to background ± SEM of four samples/group.