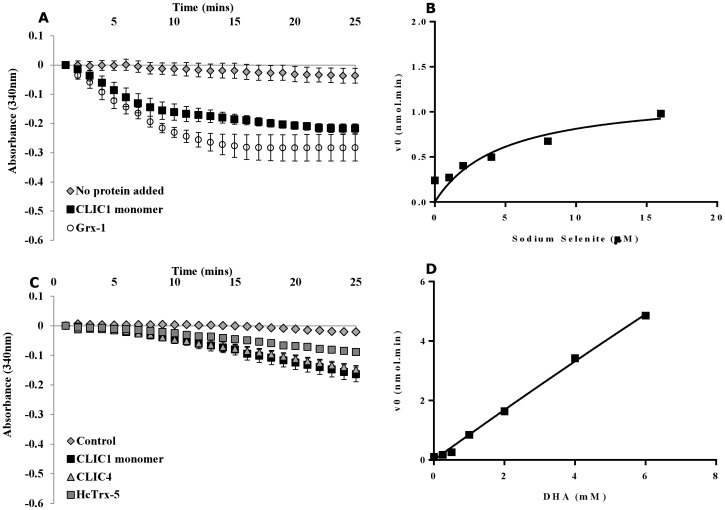
Figure 5. Sodium selenite and dehydroascorbic acid as substrates for CLIC1.
(A) The oxidoreductase enzymatic reaction using sodium selenite as a substrate was performed in 0.1 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5) with 1 mM EDTA containing 200 uM NADPH, 50 nM GR,15 uM sodium selenite, 0.1 mg/mL BSA and 5 uM CLIC1(WT) reduced monomer or 5 uM Grx-1 as a control. The reaction was initiated by the addition of 50 uM GSH at 20°C with consumption of NADPH measured at A340 nm. Error bars represent the S.E. of at least three experimental repeats. (B) The reaction was performed in 0.1 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5) with 1 mM EDTA containing 200 uM NADPH, 50 nM GR, 5 uM CLIC1 (WT) reduced monomer and sodium selenite (0, 1, 2, 4, 8 or 16 uM). The initiation of the reaction was achieved by adding 50 uM GSH at 20°C where the consumption of NADPH was measured at A340 nm. (C) The oxidoreductase enzymatic reaction using DHAR as a substrate was performed in 137 mM sodium phosphate buffer (pH 7.5) containing 2 mM EDTA, 0.35 mM NADPH, 50 nM GR, 2 mM GSH and 1 mM DHA. The reaction was initiated after addition of 5 uM reduced CLIC1, CLIC4 or HcTrx-5 (as control). Consumption of NADPH was measured at A340 nm. Error bars represent the S.E. of at least three experimental repeats. (D) DHAR activity of the CLIC proteins was determined using 137 mM sodium phosphate buffer (pH 7.5) with 2 mM EDTA, 0.35 mM NADPH, 50 nM GR, 2 mM GSH and DHA (0, 0.25, 0.5,1, 2, 4 or 6 uM). The reaction was initiated after the addition of 5 uM CLIC1 (WT) protein and the NADPH consumption was monitored at A340 nm.