Figure 4.
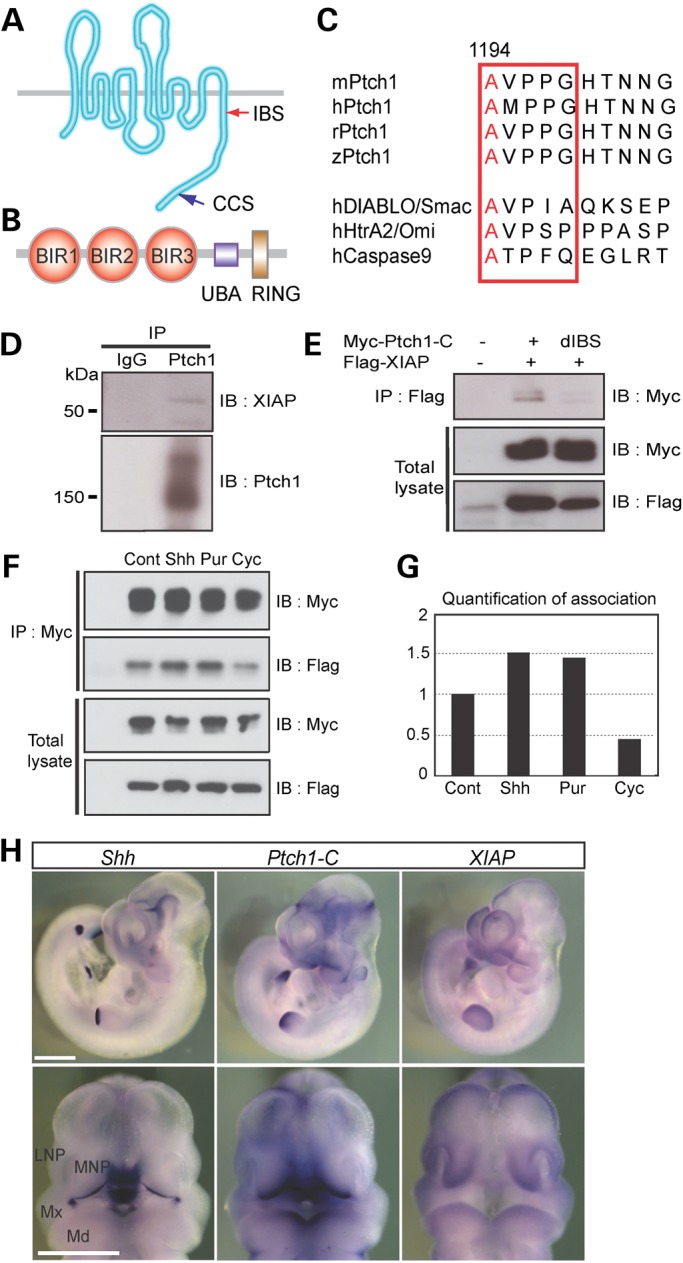
IAP-binding domain of Ptch1 associated with the BIR domain of XIAP. (A and B) Schematic representations of mouse Ptch1 (A) with IBS and caspase cleaved site (CCS) and XIAP (B) protein with Buculovirus IAP repeat domain (BIR, red circle), ubiquitin-associated domain (UBA, blue square) and RING zinc finger domain (RING, blown square). (C) Ptch1-C contains an IBS (red square) that is highly conserved and similar to known IAP-binding proteins. (D) Immunoprecipitation using Ptch1 antibody and western blot analysis of whole-cell lysates from E11.5 mouse embryos. Ptch1 interacts with XIAP. (E) Immunoprecipitation using flag antibody and western blot analysis of whole-cell lysates from myc-tagged Ptch1 C-terminal (Myc-Ptch1-C) or IBS deletion mutant (dIBS) and flag-tagged XIAP (Flag-XIAP) transfected human embryonic kidney cells (HEK293T). dIBS of Ptch1-C cannot associated with XIAP. (F) Association of Ptch1 and XIAP is affected by Shh ligand, purmorphamine (Pur, smoothened agonist) and cyclopamine (Cyc, smoothened antagonist). (G) Quantification of Ptch1 and XIAP association measured from (F). (H) Whole-mount in situ hybridization of Shh, Ptch1-C and XIAP mRNA expression in E10.5 mouse embryos. Upper panels show left side of whole embryos, whereas lower panels show frontal views. LNP, lateral nasal process; Md, mandibular process; MNP, medial nasal process; Mx, maxillary process. Scale bars: 1 mm in (H).
