Figure 1.
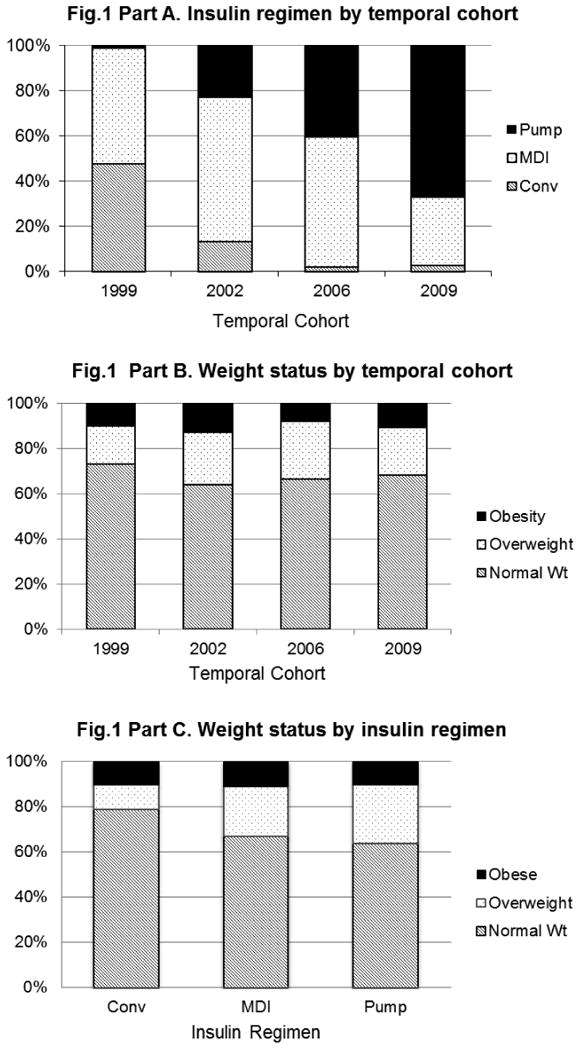
Figure 1a. Insulin regimen according to temporal cohort.
There was a significant increase in the use of intensive insulin therapy from 1999-2009.
Figure 1b. Weight status according to temporal cohort.
The prevalence of overweight/obesity in youth with type 1 diabetes remained unchanged from 1999-2009.
Figure 1c. Weight status according to insulin regimen.
There was no significant difference in weight status among youth treated with conventional therapy, multiple daily injections, or insulin pump therapy.
Conv: Conventional therapy, MDI: Multiple daily injections.
