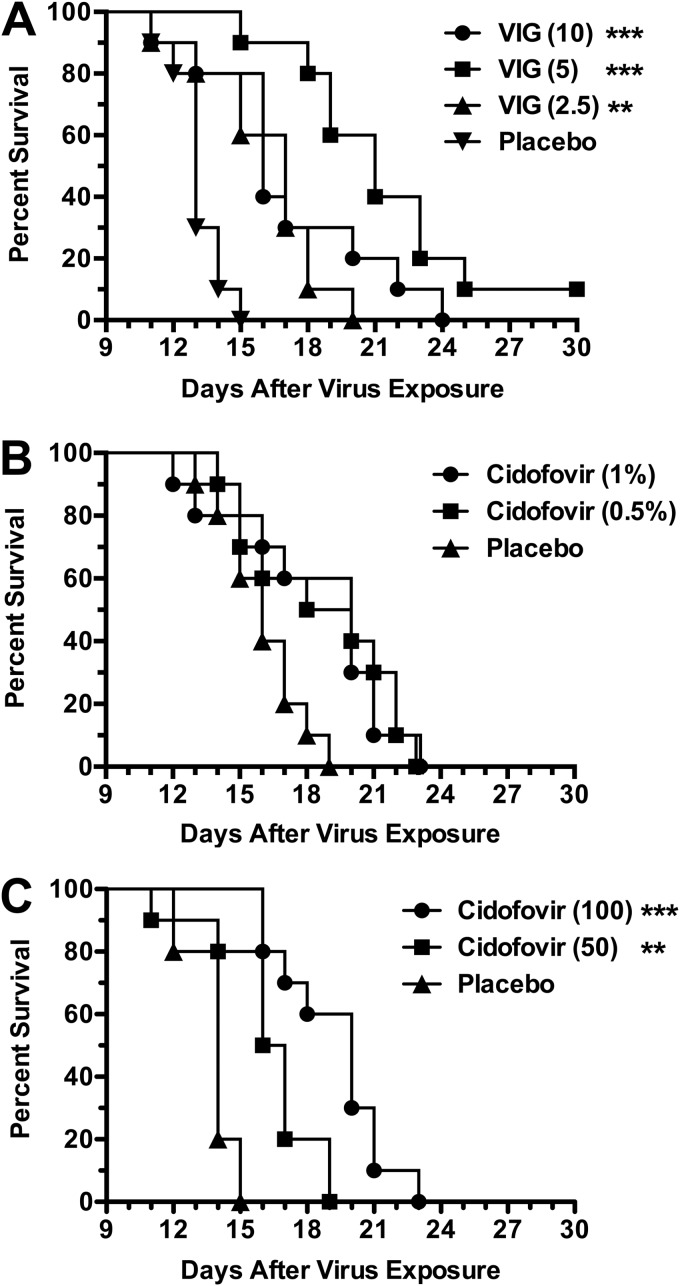
FIG 1.
Dose-response effects of VIG (A), topical CDV (B), and parenteral CDV (C) treatments on survival during cutaneous vaccinia virus infection in cyclophosphamide-immunosuppressed SHK-1 hairless mice. The mice were infected cutaneously with virus on scarified skin of the hip and shoulder regions (2.5 × 105 PFU/site in 20-μl volumes). VIG (mg/mouse) was administered parenterally once daily on days 2, 6, and 10 after infection. Topical CDV (% drug in cream formulation) was applied twice per day (at 12-h intervals) on days 2, 5, 8, and 11 after virus exposure. Parenteral CDV (mg/kg/day) was given once per day on days 2, 5, 8, and 11. The placebos consisted of parenteral saline and topical cream, administered at the same times as the other treatments. Cyclophosphamide (100 mg/kg/day) was given i.p. once per day every 4 days starting 1 day prior to virus challenge. Ten mice were in each treatment group. **, P < 0.01, and ***, P < 0.001 (both compared to placebo).