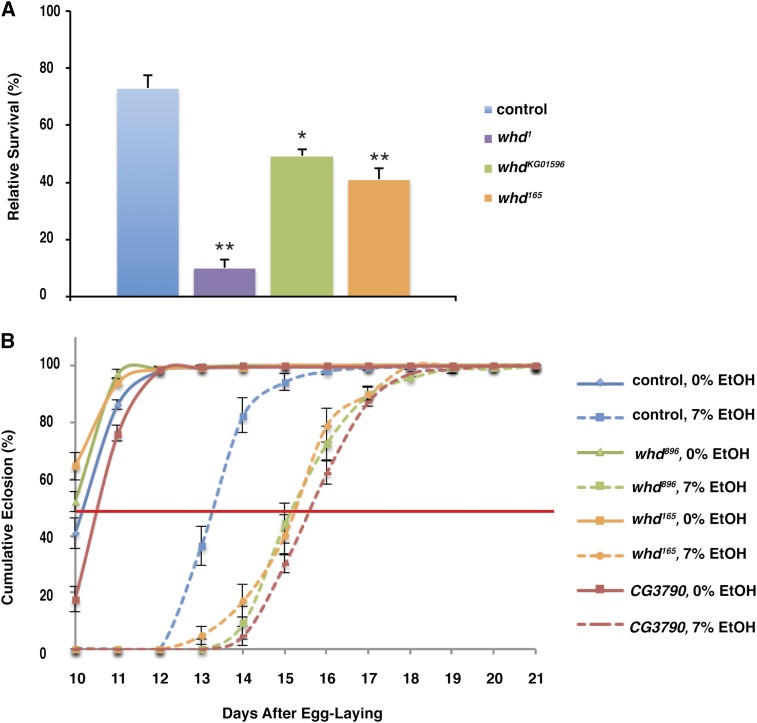
Figure 5.
whd and CG3790 mutants are sensitive to developmental ethanol effects. (A) whd mutant flies are sensitive to ethanol-induced developmental lethality. Survival has been normalized to age- and genotype-matched controls reared in ethanol-free food. N = 4. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, one-way ANOVA with Tukey HSD posthoc analysis. (B) whd165, whd896, and CG3790 mutant flies are sensitive to ethanol-induced developmental delay, taking approximately 2 additional days to reach 50% eclosion in ethanol-containing medium. Time to 50% eclosion was: WT 0% EtOH, 10.2 ± 0.1 d; WT 7% EtOH, 13.3 ± 0.14 d (P < 0.01, one-way ANOVA with Tukey HSD posthoc analysis); whd896 0% EtOH, 10.0 ± 0.07 d; whd896 7% EtOH, 15.4 d ± 0.14 d (P < 0.01 vs. both 0% controls and WT 7% EtOH-reared, one-way ANOVA with Tukey HSD post hoc analysis); whd165 0% EtOH, 9.8 ± 0.08 d; whd165 7% EtOH, 15.4 d ± 0.09 d (P < 0.01 vs. both 0% controls and WT 7% EtOH-reared, one-way ANOVA with Tukey HSD post hoc analysis); CG3790 0% EtOH, 10.6 ± 0.05 d; CG3790 7% EtOH, 15.8 d ± 0.09 d (P < 0.01 vs. both 0% controls and WT 7% EtOH-reared, one-way ANOVA with Tukey HSD post hoc analysis). Data are normalized to the total number of flies that eclosed for that treatment condition and genotype.