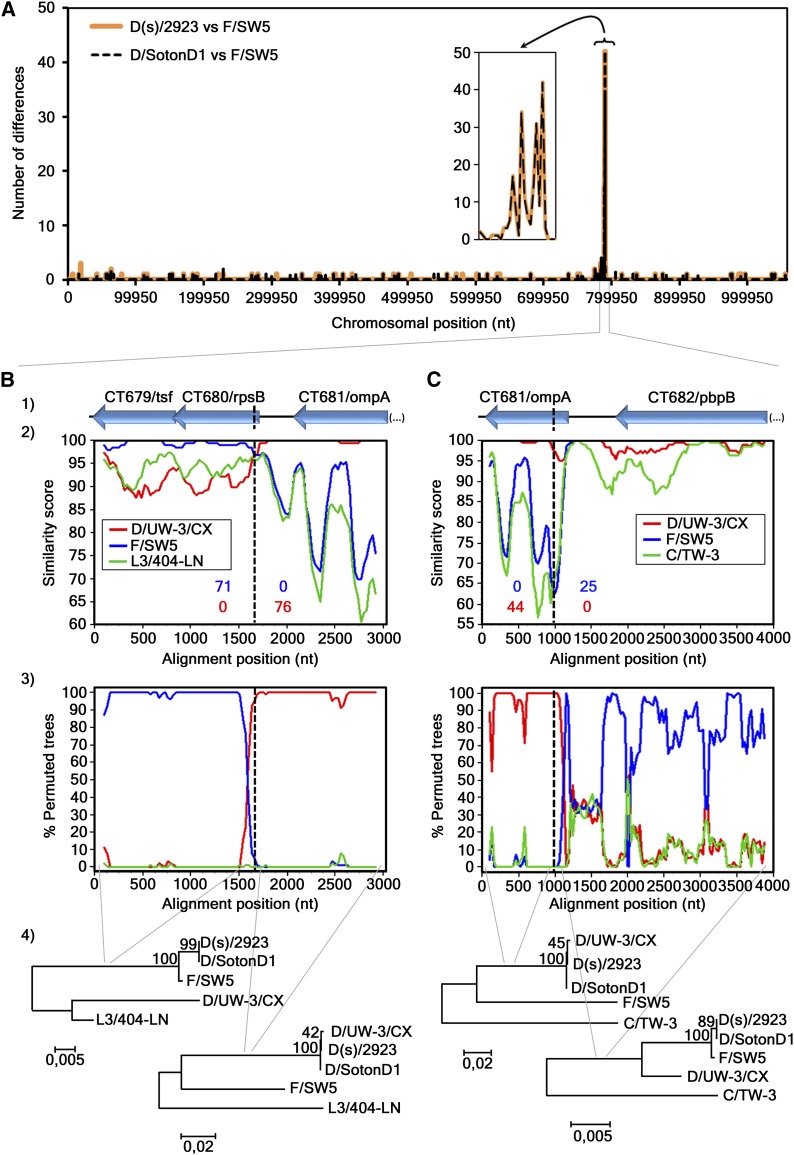
Figure 4.
Recombination analyses of the D(s)/2923 and D/SontonD1 strains. (A) Number of nucleotide differences (vertical axis) that exist between the genomic sequence of D(s)/2923 or D/SotonD1 and F/SW5. This polymorphism assessment was performed by using the DnaSP software, v5, with a window size and a step size of 1000 base pairs each. The smaller graph represents an enlarged view of the detected highly polymorphic region. (B) (first crossover) and (C) (second crossover) show the genes in each analyzed region (1) and also the results of the SimPlot (2), the BootScan (3), and the phylogenetic (4) analyses. Recombination breakpoints were individually analyzed because they were better mapped when a different outgroup strain was used for each one, i.e., the L3/404-LN for the first (B) and the C/TW-3 for the second (C) breakpoint. SimPlot graphs (2) show the level of similarity between the recombinant sequences and the respective parental strains (the number of informative sites supporting this relatedness are colored according to the graph legend box), whereas the BootScan graphs (3) show the phylogenetic relatedness (% of permuted trees) between those same sequences. Both analyses were obtained with a sliding window size of 200 bp and a step size of 30 bp. The sequence of the recombinant D strains was used as query. The vertical dashed black lines indicate the location of the estimated crossovers, shown in detail in Figure S1. Seventy-one informative sites support the similarity between the recombinant strain and F/SW5, whereas 76 support its similarity with D/UW-3/CX (P = 9.28 × 10−44). Forty-four informative sites support the similarity between the recombinant strain and D/UW-3/CX, whereas 25 support its similarity with F/SW5 (P = 6.65 × 10−19). In these defined regions there are no informative sites supporting the alternative hypotheses. The phylogenetic trees (4) were constructed with the nucleotide sequences adjacent to each estimated breakpoint region (NJ method; Kimura 2-parameter method; bootstrap = 1000) and support the recombination event.